Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch
基础知识
倒排索引
- 正向索引
- mysql采用的是正向索引
- 如果根据id查,直接走索引,速度非常快
- 如果做模糊查询,逐行扫描全表,效率低
- 倒排索引
- 创建倒排索引,是对正向索引的一种特殊处理
- 将每一个文档的数据利用算法分词,得到一个个词条
- 创建词条表,每行数据包括词条、词条所在文档id、位置等信息
- 因为词条唯一性,可以给词条创建索引,例如hash表结构索引
- 倒排索引的搜索流程
- 对用户输入内容分词,得到词条
- 拿着词条在倒排索引中查找,可以得到包含词条的文档id
- 拿着文档id到正向索引中查找具体文档
- 创建倒排索引,是对正向索引的一种特殊处理
- 对比
- 正向索引是最传统的,根据id索引的方式。但根据词条查询时,必须先逐条获取每个文档,然后判断文档中是否包含所需要的词条,是根据文档找词条的过程
- 倒排索引则相反,是先找到用户要搜索的词条,根据词条得到保护词条的文档的id,然后根据id获取文档。是根据词条找文档的过程
- 正向索引
- 优点:
- 可以给多个字段创建索引
- 根据索引字段搜索、排序速度非常快
- 缺点:
- 根据非索引字段,或者索引字段中的部分词条查找时,只能全表扫描
- 优点:
- 倒排索引
- 优点:
- 根据词条搜索、模糊搜索时,速度非常快
- 缺点:
- 只能给词条创建索引,而不是字段
- 无法根据字段做排序
- 优点:
概念
- 文档(Document),对应mysql的行
- 字段(Field),对应mysql中的列
- 索引(Index),对应mysql中的表
- 映射(mapping),对应mysql中表的结构约束
| MySQL | Elasticsearch | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Table | Index | 索引(index),就是文档的集合,类似数据库的表(table) |
| Row | Document | 文档(Document),就是一条条的数据,类似数据库中的行(Row),文档都是JSON格式 |
| Column | Field | 字段(Field),就是JSON文档中的字段,类似数据库中的列(Column) |
| Schema | Mapping | Mapping(映射)是索引中文档的约束,例如字段类型约束。类似数据库的表结构(Schema) |
| SQL | DSL | DSL是elasticsearch提供的JSON风格的请求语句,用来操作elasticsearch,实现CRUD |
- Mysql:擅长事务类型操作,可以确保数据的安全和一致性
- Elasticsearch:擅长海量数据的搜索、分析、计算
- 应用
- 对安全性要求较高的写操作,使用mysql实现
- 对查询性能要求较高的搜索需求,使用elasticsearch实现
- 两者再基于某种方式,实现数据的同步,保证一致性
ik分词器
分词器的作用是什么?
- 创建倒排索引时对文档分词
- 用户搜索时对输入的内容分词
IK分词器有几种模式?
ik_smart:智能切分,粗粒度
ik_max_word:最细切分,细粒度
IK分词器如何拓展词条?如何停用词条?
利用config目录的IkAnalyzer.cfg.xml文件添加拓展词典和停用词典
在词典中添加拓展词条或者停用词条
mapping映射属性
mapping是对索引库中文档的约束,常见的mapping属性包括:
type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:
- 字符串:text(可分词的文本)、keyword(精确值,例如:品牌、国家、ip地址)
- 数值:long、integer、short、byte、double、float、half_float、scaled_float(高精度)
- 布尔:boolean
- 日期:date
- 数组:Array
- 对象:object
- 经纬度
- geo_point:由纬度(latitude)和经度(longitude)确定的一个点。例如:"32.8752345, 120.2981576"
- •geo_shape:有多个geo_point组成的复杂几何图形。例如一条直线,"LINESTRING (-77.03653 38.897676, -77.009051 38.889939)"
index:是否创建索引,默认为true(字段会被索引,则可以用来进行搜索)
store :是否将数据进行独立存储,默认为 false
原始的文本会存储在_source 里面,默认情况下其他提取出来的字段都不是独立存储的,是从 _source 里面提取出来的。当"store": true 时,获取独立存储的字段要比从 _source 中解析快得多,但是也会占用更多的空间
analyzer:使用哪种分词器
properties:该字段的子字段
copy_to:将多个字段的值利用copy_to合并,形成新的字段,提供给用户搜索,查询到的结果中无此字段
format:针对时间类型可以设置
- 默认支持的格式(
yyyy、yyyyMM、yyyyMMdd、yyyyMMddHHmmss、yyyy-MM、yyyy-MM-dd、yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss、yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.SSS、yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.SSSZ、时间戳) --- 不需要用format - 其他格式的就要用
"format":"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"(epoch_millis表示时间戳)
- 默认支持的格式(
{
"age": 21,
"weight": 52.1,
"isMarried": false,
"info": "黑马程序员Java讲师",
"email": "zy@itcast.cn",
"score": [99.1, 99.5, 98.9],
"name": {
"firstName": "云",
"lastName": "赵"
}
}
对应的每个字段映射(mapping):
- age:类型为 integer;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- weight:类型为float;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- isMarried:类型为boolean;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- info:类型为字符串,需要分词,因此是text;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;分词器可以用ik_smart
- email:类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;不参与搜索,因此需要index为false;无需分词器
- score:虽然是数组,但是我们只看元素的类型,类型为float;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- name:类型为object,需要定义多个子属性
- name.firstName;类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- name.lastName;类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
分词器
默认的拼音分词器会将每个汉字单独分为拼音,而我们希望的是每个词条形成一组拼音,需要对拼音分词器做个性化定制,形成自定义分词器
elasticsearch中分词器(analyzer)的组成包含三部分:
- character filters:在tokenizer之前对文本进行处理。例如删除字符、替换字符
- tokenizer:将文本按照一定的规则切割成词条(term)。例如keyword,就是不分词;还有ik_smart
- tokenizer filter:将tokenizer输出的词条做进一步处理。例如大小写转换、同义词处理、拼音处理等
文档分词时会依次由这三部分来处理文档

声明自定义分词器的语法如下
PUT /test
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": { // 自定义分词器
"my_analyzer": { // 分词器名称
"tokenizer": "ik_max_word", //分词
"filter": "py" //分词后处理
}
},
"filter": { // 自定义tokenizer filter
"py": { // 过滤器名称
"type": "pinyin", // 过滤器类型,这里是pinyin
"keep_full_pinyin": false,
"keep_joined_full_pinyin": true,
"keep_original": true,
"limit_first_letter_length": 16,
"remove_duplicated_term": true,
"none_chinese_pinyin_tokenize": false
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "my_analyzer",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
}
}
}
}
拼音分词器注意事项
- 为了避免搜索到同音字,搜索时不要使用拼音分词器
DSL操作
CURD操作
索引库的CRUD
创建索引库和映射
基本语法:
- 请求方式:PUT
- 请求路径:/索引库名,可以自定义
- 请求参数:mapping映射
格式:
PUT /索引库名称
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"字段名":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"字段名2":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": "false"
},
"字段名3":{
"properties": {
"子字段": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
// ...略
}
}
}
示例:
PUT /heima
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"info":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"email":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": "falsae"
},
"name":{
"properties": {
"firstName": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
// ... 略
}
}
}
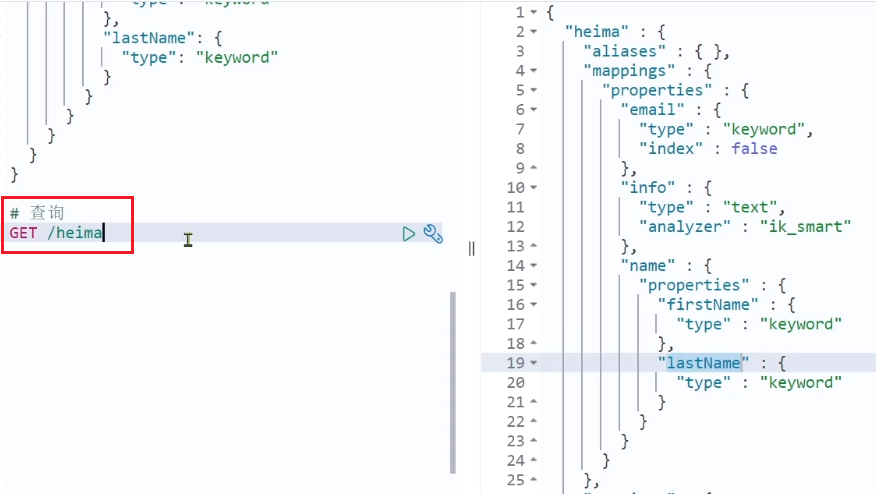
查询索引库
基本语法:
请求方式:GET
请求路径:/索引库名
请求参数:无
格式:
GET /索引库名
示例:
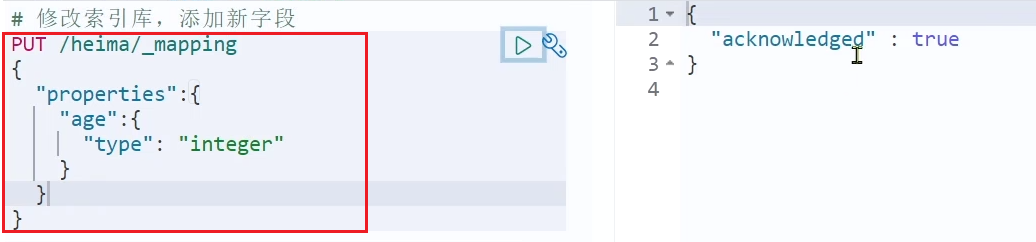
修改索引库
倒排索引结构虽然不复杂,但是一旦数据结构改变(比如改变了分词器),就需要重新创建倒排索引,这简直是灾难。因此索引库一旦创建,无法修改mapping
虽然无法修改mapping中已有的字段,但是却允许添加新的字段到mapping中,因为不会对倒排索引产生影响。
语法说明:
PUT /索引库名/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"新字段名":{
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
示例:
删除索引库
语法:
请求方式:DELETE
请求路径:/索引库名
请求参数:无
格式:
DELETE /索引库名
文档的CRUD
新增文档
语法:
POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id
{
"字段1": "值1",
"字段2": "值2",
"字段3": {
"子属性1": "值3",
"子属性2": "值4"
},
// ...
}
示例:
POST /heima/_doc/1
{
"info": "黑马程序员Java讲师",
"email": "zy@itcast.cn",
"name": {
"firstName": "云",
"lastName": "赵"
}
}
响应:
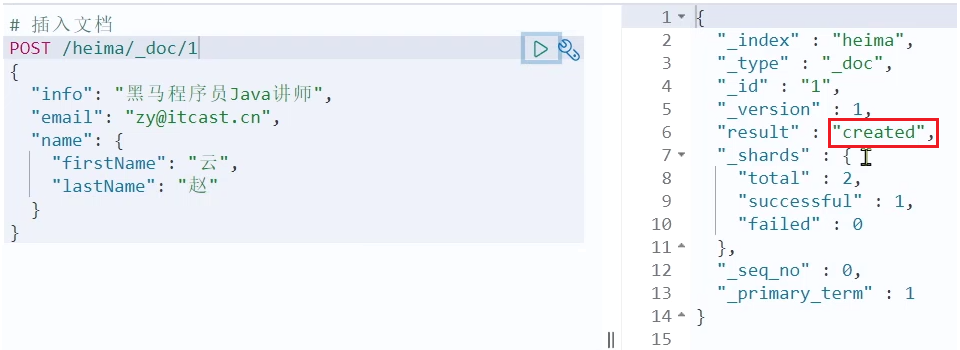
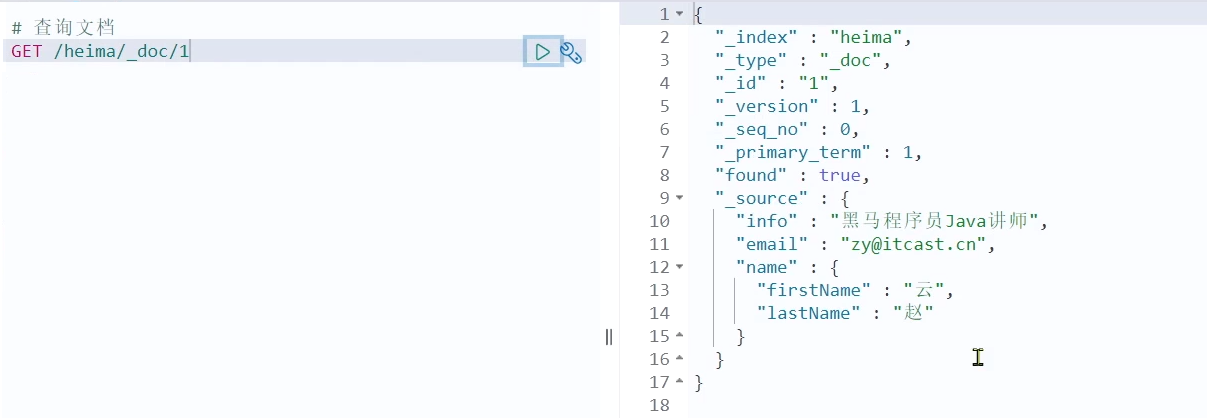
查询文档
根据rest风格,新增是post,查询应该是get,不过查询一般都需要条件,这里我们把文档id带上。
语法:
GET /{索引库名称}/_doc/{id}
通过kibana查看数据:
GET /heima/_doc/1
查看结果:
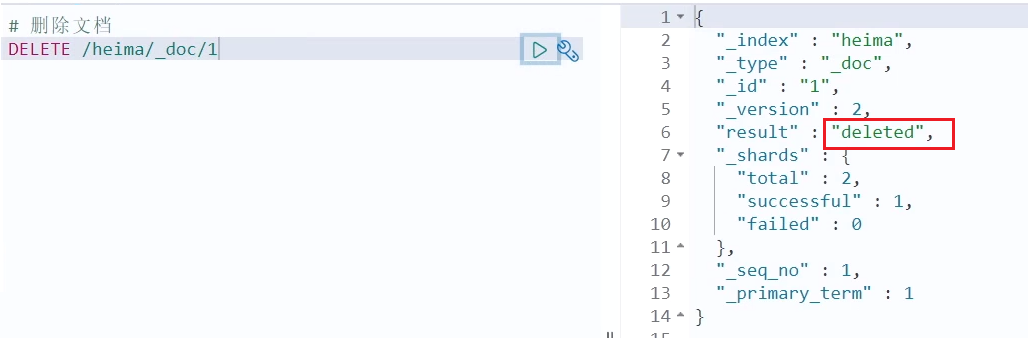
删除文档
删除使用DELETE请求,同样,需要根据id进行删除:
语法:
DELETE /{索引库名}/_doc/id值
示例:
## 根据id删除数据
DELETE /heima/_doc/1
结果:
修改文档
修改有两种方式:
- 全量修改:直接覆盖原来的文档
- 增量修改:修改文档中的部分字段
全量修改
全量修改是覆盖原来的文档,其本质是:
- 根据指定的id删除文档
- 新增一个相同id的文档
注意:如果根据id删除时,id不存在,第二步的新增也会执行,也就从修改变成了新增操作了
语法:
PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
{
"字段1": "值1",
"字段2": "值2",
// ... 略
}
示例:
PUT /heima/_doc/1
{
"info": "黑马程序员高级Java讲师",
"email": "zy@itcast.cn",
"name": {
"firstName": "云",
"lastName": "赵"
}
}
增量修改
增量修改是只修改指定id匹配的文档中的部分字段。
语法:
POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id
{
"doc": {
"字段名": "新的值",
}
}
示例:
POST /heima/_update/1
{
"doc": {
"email": "ZhaoYun@itcast.cn"
}
}
总结
创建索引库:PUT /索引库名
查询索引库:GET /索引库名
删除索引库:DELETE /索引库名
添加字段:PUT /索引库名/_mapping
创建文档:POST /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
查询文档:GET /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
删除文档:DELETE /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
修改文档:
- 全量修改:PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
- 增量修改:POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id { "doc": {字段}}
搜索操作
查询所有:查询出所有数据,一般测试用。例如:match_all
全文检索(full text)查询:利用分词器对用户输入内容分词,然后去倒排索引库中匹配。例如:
- match_query
- multi_match_query
精确查询:根据精确词条值查找数据,一般是查找keyword、数值、日期、boolean等类型字段。例如:
- ids
- range
- term
地理(geo)查询:根据经纬度查询。例如:
- geo_distance
- geo_bounding_box
复合(compound)查询:复合查询可以将上述各种查询条件组合起来,合并查询条件。例如:
- bool
- function_score
查询的语法基本一致:
GET /indexName/_search
{
"query": {
"查询类型": {
"查询条件": "条件值"
}
}
}
查询所有
- 查询类型为match_all
- 没有查询条件
// 查询所有
GET /indexName/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}
全文检索
全文检索查询的基本流程如下:
- 对用户搜索的内容做分词,得到词条
- 根据词条去倒排索引库中匹配,得到文档id
- 根据文档id找到文档,返回给用户
比较常用的场景包括:
- 商城的输入框搜索
- 百度输入框搜索
因为是拿着词条去匹配,因此参与搜索的字段也必须是可分词的text类型的字段
常见的全文检索查询包括:
match查询:单字段查询
GET /indexName/_search { "query": { "match": { "FIELD": "TEXT" } } }multi_match查询:多字段查询,任意一个字段符合条件就算符合查询条件
GET /indexName/_search { "query": { "multi_match": { "query": "TEXT", "fields": ["FIELD1", " FIELD12"] } } }
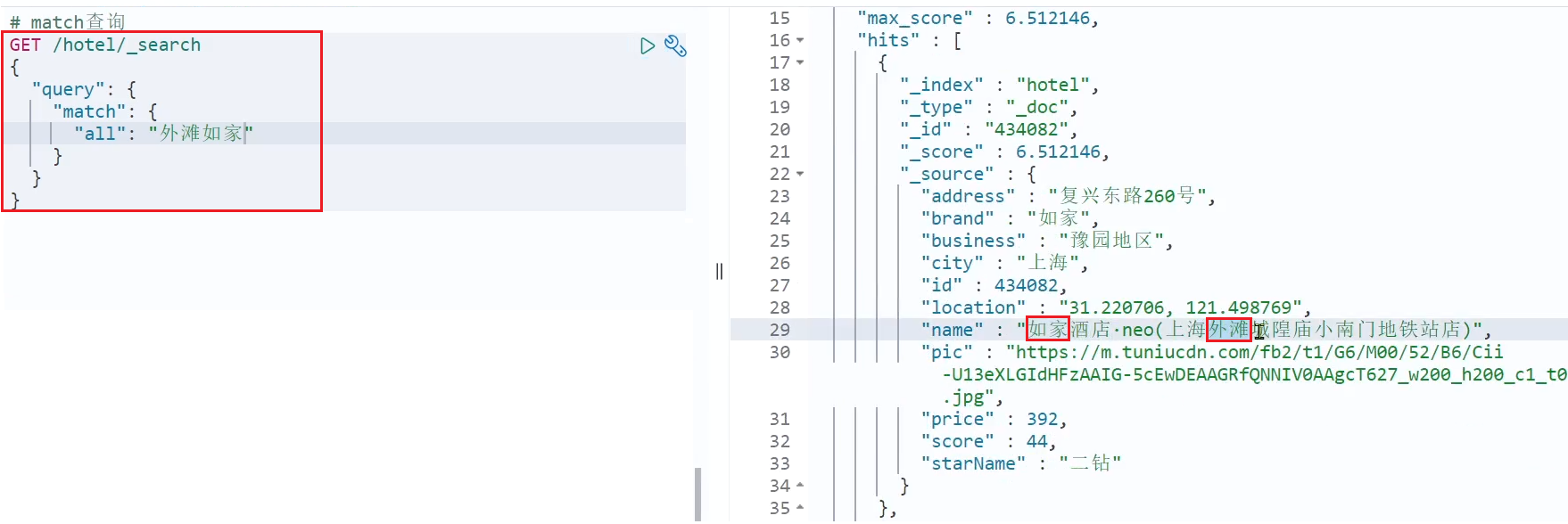
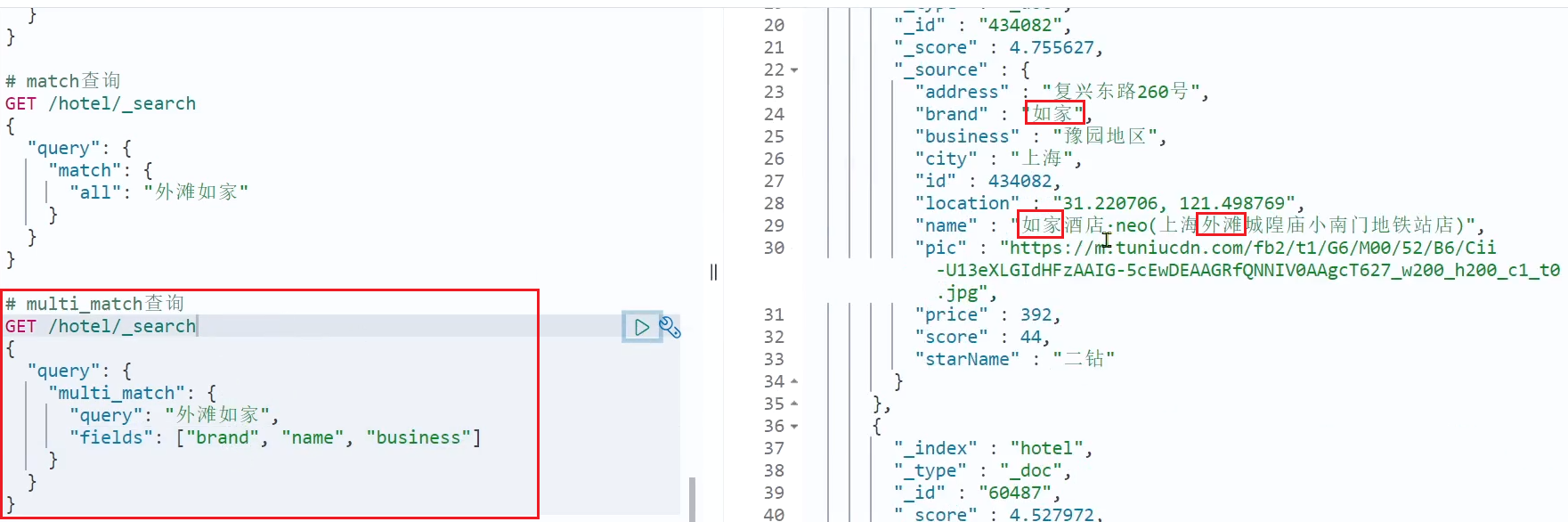
两种查询结果是一样,由于copy_to,但是,搜索字段越多,对查询性能影响越大,因此建议采用copy_to,然后单字段查询的方式
精确查询
精确查询一般是查找keyword、数值、日期、boolean等类型字段。所以不会对搜索条件分词。常见的有:
term:根据词条精确值查询
// term查询 GET /indexName/_search { "query": { "term": { "FIELD": { "value": "VALUE" } } } }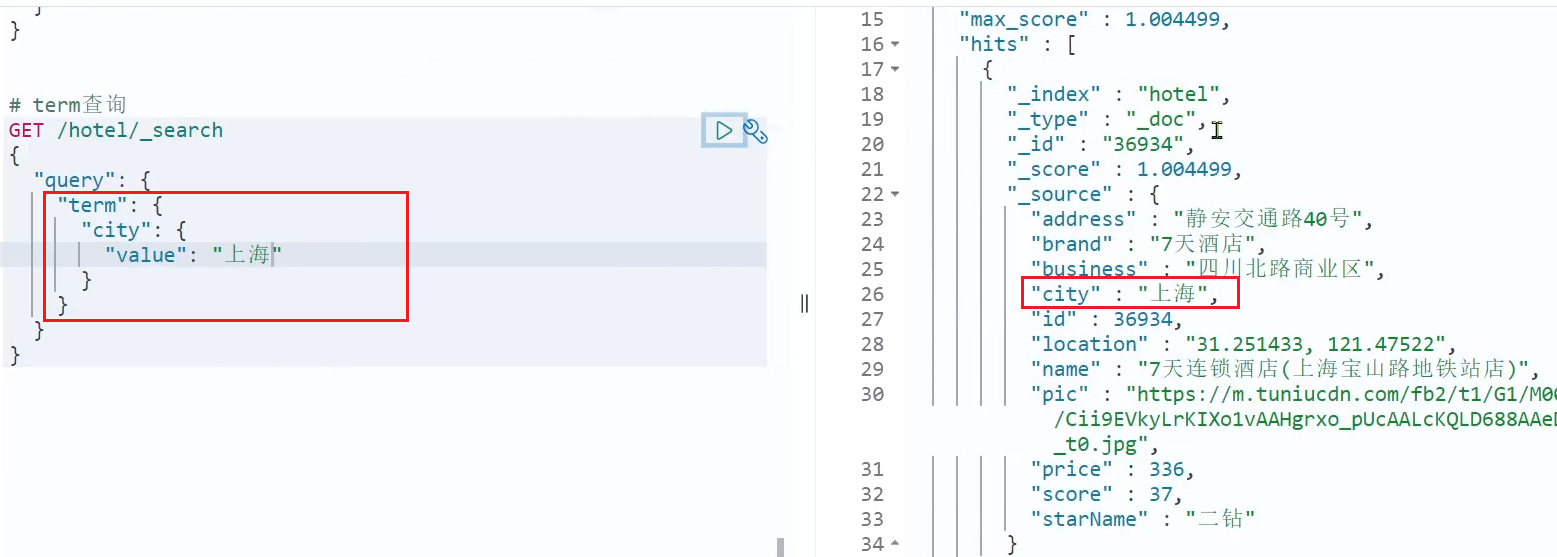
image-20221007205042359 range:根据值的范围查询
// range查询 GET /indexName/_search { "query": { "range": { "FIELD": { "gte": 10, // 这里的gte代表大于等于,gt则代表大于 "lte": 20 // lte代表小于等于,lt则代表小于 } } } }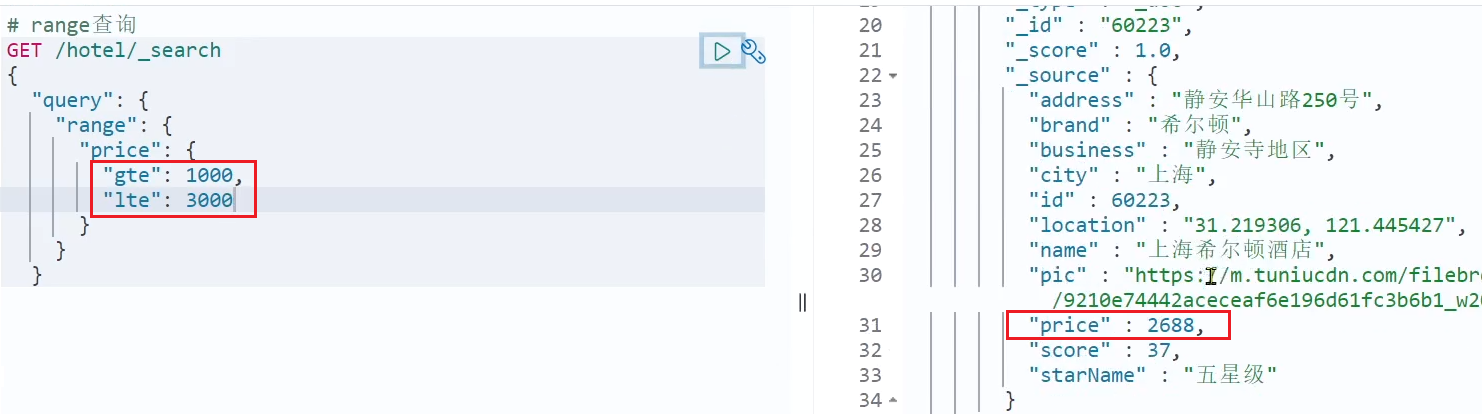
image-20221007205140401
地理坐标查询
常见的使用场景包括:
携程:搜索我附近的酒店
滴滴:搜索我附近的出租车
微信:搜索我附近的人
geo_bounding_box:矩形范围查询,查询坐标落在某个矩形范围的所有文档:
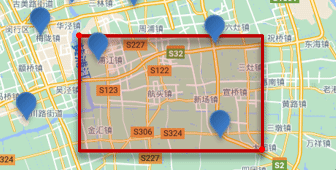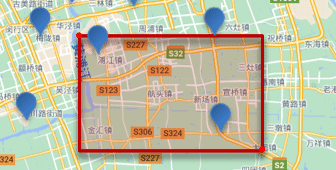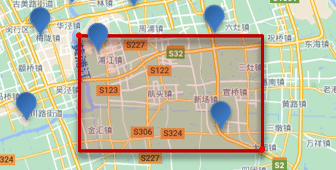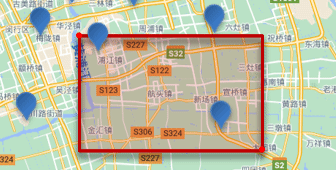
查询时,需要指定矩形的左上、右下两个点的坐标,然后画出一个矩形,落在该矩形内的都是符合条件的点
// geo_bounding_box查询 GET /indexName/_search { "query": { "geo_bounding_box": { "FIELD": { "top_left": { // 左上点 "lat": 31.1, "lon": 121.5 }, "bottom_right": { // 右下点 "lat": 30.9, "lon": 121.7 } } } } }geo_distance:附近查询,也叫做距离查询,查询到指定中心点小于某个距离值的所有文档
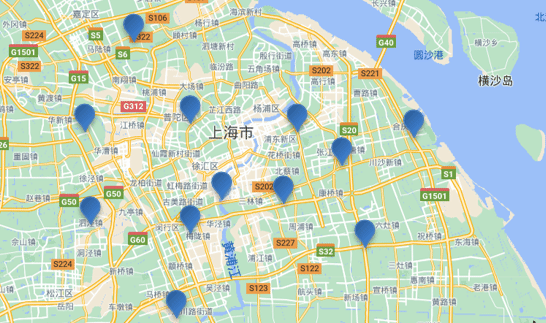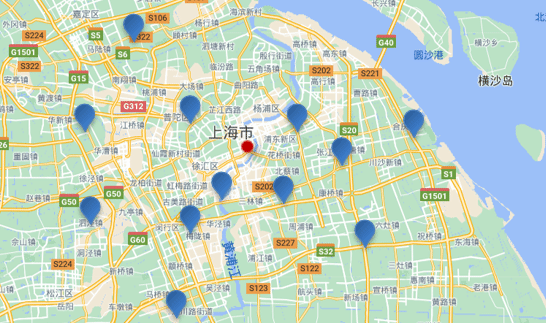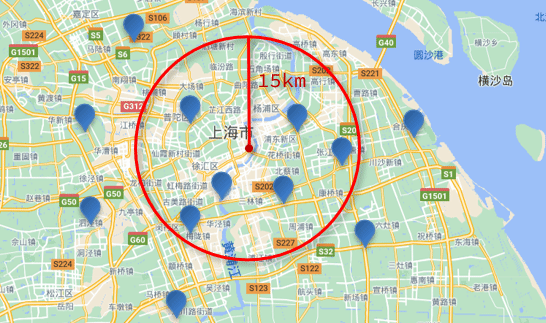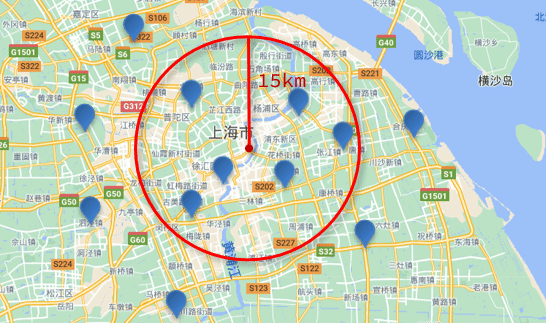
// geo_distance 查询 GET /indexName/_search { "query": { "geo_distance": { "distance": "15km", // 半径 "FIELD": "31.21,121.5" // 圆心 } } }
复合查询
相关性算分:当我们利用match查询时,文档结果会根据与搜索词条的关联度打分(_score),返回结果时按照分值降序排列
早期使用的打分算法是TF-IDF算法,公式如下:

image-20210721190152134 在后来的5.1版本升级中,elasticsearch将算法改进为BM25算法,公式如下:

image-20210721190416214 TF-IDF算法有一各缺陷,就是词条频率越高,文档得分也会越高,单个词条对文档影响较大。而BM25则会让单个词条的算分有一个上限,曲线更加平滑:
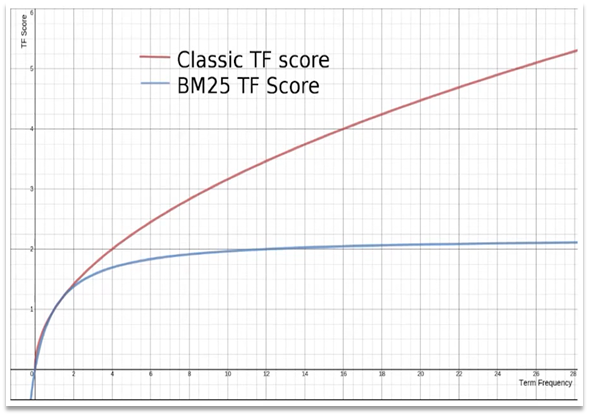
image-20210721190907320 function_score: 算分函数查询,四部分组成
原始查询条件:query部分,基于这个条件搜索文档,并且基于BM25算法给文档打分,原始算分(query score)
过滤条件:filter部分,符合该条件的文档才会重新算分
算分函数:符合filter条件的文档要根据这个函数做运算,得到的函数算分(function score),有四种函数
- weight:函数结果是常量
- field_value_factor:以文档中的某个字段值作为函数结果
- random_score:以随机数作为函数结果
- script_score:自定义算分函数算法
运算模式:算分函数的结果、原始查询的相关性算分,两者之间的运算方式,包括:
- multiply:相乘
- replace:用function score替换query score
- 其它,例如:sum、avg、max、min
function score的运行流程如下:
- 1)根据原始条件查询搜索文档,并且计算相关性算分,称为原始算分(query score)
- 2)根据过滤条件,过滤文档
- 3)符合过滤条件的文档,基于算分函数运算,得到函数算分(function score)
- 4)将原始算分(query score)和函数算分(function score)基于运算模式做运算,得到最终结果,作为相关性算分
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "function_score": { "query": { .... }, // 原始查询,可以是任意条件 "functions": [ // 算分函数 { "filter": { // 满足的条件,品牌必须是如家 "term": { "brand": "如家" } }, "weight": 2 // 算分权重为2 } ], "boost_mode": "sum" // 加权模式,求和 } } }bool:布尔查询,是一个或多个查询子句的组合,每一个子句就是一个子查询。子查询的组合方式有:
- must:必须匹配每个子查询,类似“与”
- should:选择性匹配子查询,类似“或”
- must_not:必须不匹配,不参与算分,类似“非”,常用在不大于...
- filter:必须匹配,不参与算分,类似“与”,常用于大于...
每一个不同的字段,其查询的条件、方式都不一样,必须是多个不同的查询,而要组合这些查询,就必须用bool查询了。
需要注意的是,搜索时,参与打分的字段越多,查询的性能也越差。因此这种多条件查询时,建议这样做:
- 搜索框的关键字搜索,是全文检索查询,使用must查询,参与算分
- 其它过滤条件,采用filter查询。不参与算分
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "bool": { "must": [ {"term": {"city": "上海" }} ], "should": [ {"term": {"brand": "皇冠假日" }}, {"term": {"brand": "华美达" }} ], "must_not": [ { "range": { "price": { "lte": 500 } }} ], "filter": [ { "range": {"score": { "gte": 45 } }} ] } } }
结果处理
排序
默认是根据相关度算分(_score)来排序,但是也支持自定义方式对搜索结果排序。可以排序字段类型有:keyword类型、数值类型、地理坐标类型、日期类型等
普通字段排序
排序条件是一个数组,也就是可以写多个排序条件。按照声明的顺序,当第一个条件相等时,再按照第二个条件排序,以此类推
GET /indexName/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "sort": [ { "FIELD": "desc" // 排序字段、排序方式ASC、DESC } ] }
image-20221007211039471 地理坐标排序
结果返回的sort就是距离目标点的距离
获取你的位置的经纬度的方式:https://lbs.amap.com/demo/jsapi-v2/example/map/click-to-get-lnglat/
GET /indexName/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "sort": [ { "_geo_distance" : { "FIELD" : "纬度,经度", // 文档中geo_point类型的字段名、目标坐标点 "order" : "asc", // 排序方式 "unit" : "km" // 排序的距离单位 } } ] }
分页
elasticsearch 默认情况下只返回top10的数据。而如果要查询更多数据就需要修改分页参数了。elasticsearch中通过修改from、size参数来控制要返回的分页结果:
- from:从第几个文档开始
- size:总共查询几个文档
类似于mysql中的limit ?, ?
基本分页
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "from": 0, // 分页开始的位置,默认为0 "size": 10, // 期望获取的文档总数 "sort": [ {"price": "asc"} ] }深度分页存在的问题
- 我要查询990~1000的数据,查询逻辑要这么写:
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} }, "from": 990, // 分页开始的位置,默认为0 "size": 10, // 期望获取的文档总数 "sort": [ {"price": "asc"} ] }这里是查询990开始的数据,也就是 第990~第1000条 数据
不过,elasticsearch内部分页时,必须先查询 0~1000条,然后截取其中的990 ~ 1000的这10条:
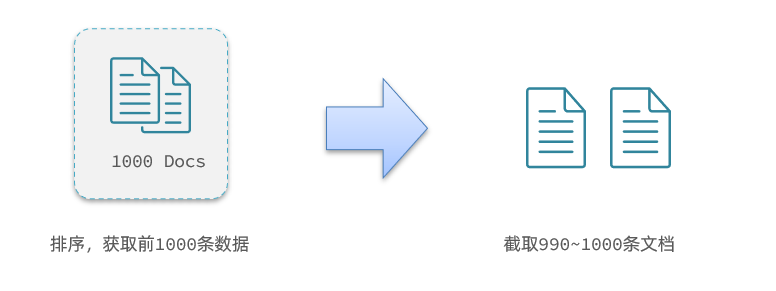
image-20210721200643029 查询TOP1000,如果es是单点模式,这并无太大影响
但是elasticsearch将来一定是集群,例如我集群有5个节点,我要查询TOP1000的数据,并不是每个节点查询200条就可以了
因为节点A的TOP200,在另一个节点可能排到10000名以外了
因此要想获取整个集群的TOP1000,必须先查询出每个节点的TOP1000,汇总结果后,重新排名,重新截取TOP1000
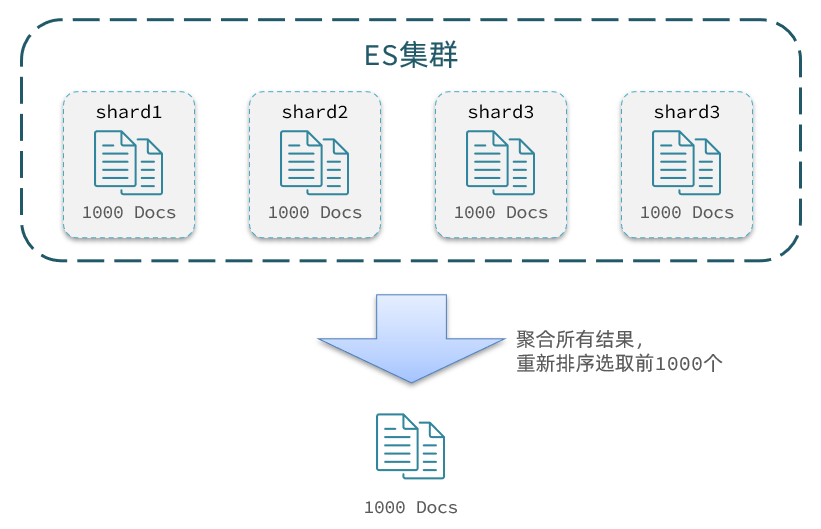
image-20210721201003229 那如果我要查询9900~10000的数据呢?是不是要先查询TOP10000呢?那每个节点都要查询10000条?汇总到内存中?
当查询分页深度较大时,汇总数据过多,对内存和CPU会产生非常大的压力,因此elasticsearch会禁止from+ size 超过10000的请求
针对深度分页,ES提供了两种解决方案,官方文档:
search after:分页时需要排序,原理是从上一次的排序值开始,查询下一页数据。官方推荐使用的方式
- 存在的问题,只能往后查,往前查仍然需要排序
scroll:原理将排序后的文档id形成快照,保存在内存。官方已经不推荐使用
高亮
- 原理
- 给文档中的所有关键字都添加一个标签,例如
<em>标签 - 页面给
<em>标签编写CSS样式
- 给文档中的所有关键字都添加一个标签,例如
GET /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"FIELD": "TEXT" // 查询条件,高亮一定要使用全文检索查询
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": { // 指定要高亮的字段
"FIELD": {
"pre_tags": "<em>", // 用来标记高亮字段的前置标签
"post_tags": "</em>" // 用来标记高亮字段的后置标签
}
}
}
}
注意:
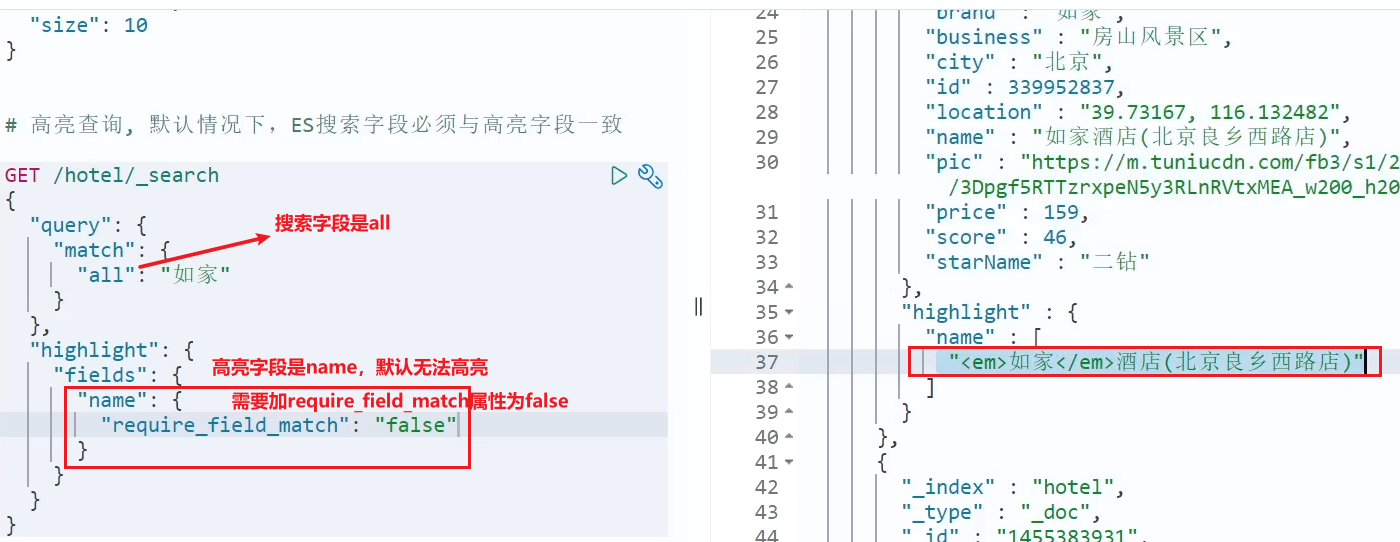
- 高亮是对关键字高亮,因此搜索条件必须带有关键字,而不能是范围这样的查询。
- 默认情况下,高亮的字段,必须与搜索指定的字段一致,否则无法高亮
- 如果要对非搜索字段高亮,则需要添加一个属性:required_field_match=false
总结
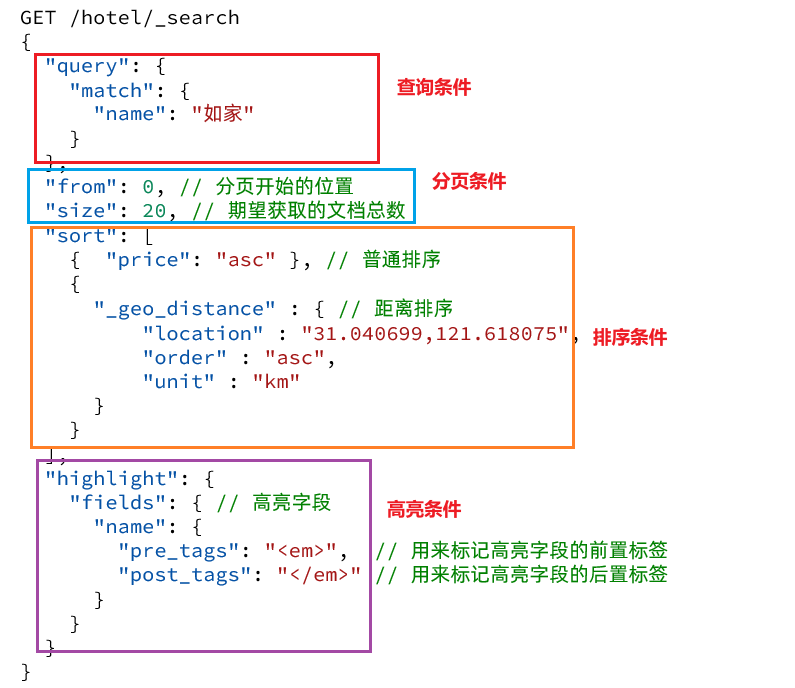
查询的DSL是一个大的JSON对象,包含下列属性:
- query:查询条件
- from和size:分页条件
- sort:排序条件
- highlight:高亮条件
示例:
数据聚合
**聚合(aggregations)**可以让我们极其方便的实现对数据的统计、分析、运算
种类
- **桶(Bucket)**聚合:用来对文档做分组
- TermAggregation:按照文档字段值分组,例如按照品牌值分组、按照国家分组
- Date Histogram:按照日期阶梯分组,例如一周为一组,或者一月为一组
- **度量(Metric)**聚合:用以计算一些值,比如:最大值、最小值、平均值等
- Avg:求平均值
- Max:求最大值
- Min:求最小值
- Stats:同时求max、min、avg、sum等
- **管道(pipeline)**聚合:其它聚合的结果为基础做聚合
**注意:**参加聚合的字段必须是keyword、日期、数值、布尔类型
- **桶(Bucket)**聚合:用来对文档做分组
Bucket聚合
GET /hotel/_search
{
"size": 0, // 设置size为0,结果中不包含文档,只包含聚合结果
"aggs": { // 定义聚合
"brandAgg": { //给聚合起个名字
"terms": { // 聚合的类型,按照品牌值聚合,所以选择term
"field": "brand", // 参与聚合的字段
"size": 20 // 希望获取的聚合结果数量
}
}
}
}

对聚合结果排序
默认情况下,Bucket聚合会统计Bucket内的文档数量,记为_count,并且按照_count降序排序。
我们可以指定order属性,自定义聚合的排序方式
GET /hotel/_search { "size": 0, "aggs": { "brandAgg": { "terms": { "field": "brand", "order": { "_count": "asc" // 按照_count升序排列 }, "size": 20 } } } }限定聚合范围
默认情况下,Bucket聚合是对索引库的所有文档做聚合,但真实场景下,用户会输入搜索条件,因此聚合必须是对搜索结果聚合。那么聚合必须添加限定条件
我们可以限定要聚合的文档范围,只要添加query条件即可,聚合得到的品牌明显变少了
GET /hotel/_search { "query": { "range": { "price": { "lte": 200 // 只对200元以下的文档聚合 } } }, "size": 0, "aggs": { "brandAgg": { "terms": { "field": "brand", "size": 20 } } } }
Metric聚合
对桶内的文档做运算,获取每个的min、max、avg等值
这就要用到Metric聚合了,例如stat聚合:就可以获取min、max、avg等结果
GET /hotel/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"brandAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "brand",
"size": 20
},
"aggs": { // 是brands聚合的子聚合,也就是分组后对每组分别计算
"score_stats": { // 聚合名称
"stats": { // 聚合类型,这里stats可以计算min、max、avg等
"field": "score" // 聚合字段,这里是score
}
}
}
}
}
}
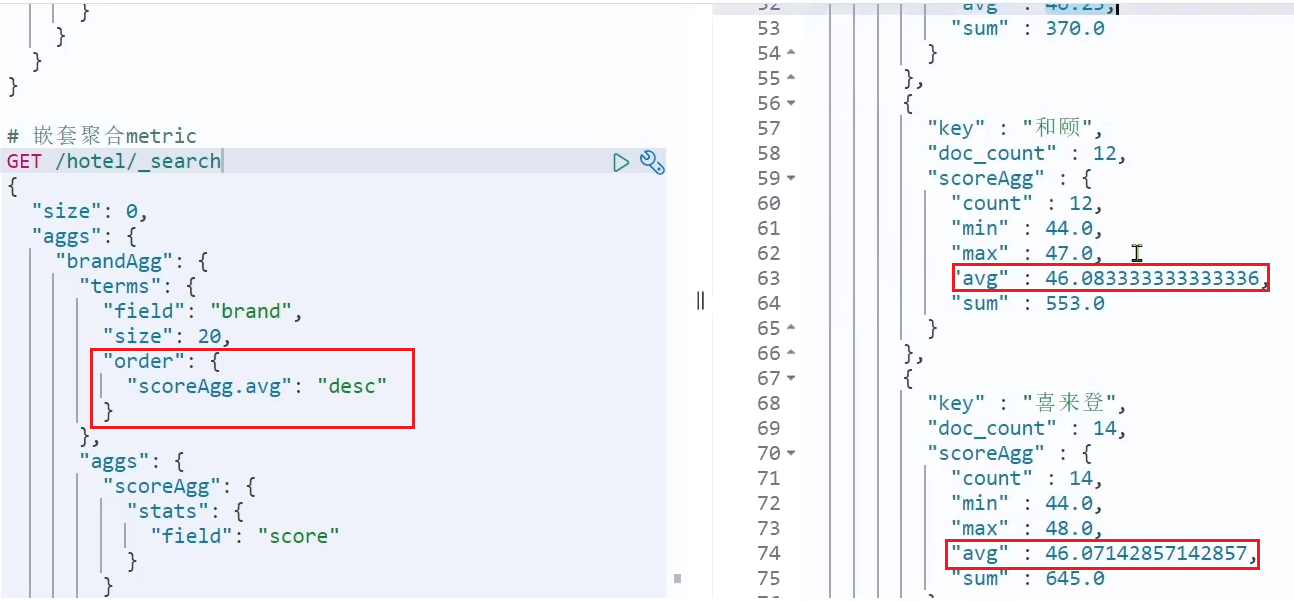
这次的score_stats聚合是在brandAgg的聚合内部嵌套的子聚合。因为我们需要在每个桶分别计算
另外,我们还可以给聚合结果做个排序,例如按照每个桶的酒店平均分做排序
自动补全
elasticsearch提供了Completion Suggester查询来实现自动补全功能。这个查询会匹配以用户输入内容开头的词条并返回。为了提高补全查询的效率,对于文档中字段的类型有一些约束:
参与补全查询的字段必须是completion类型。
字段的内容一般是用来补全的多个词条形成的数组。
比如,一个这样的索引库:
// 创建索引库
PUT test
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title":{
"type": "completion"
}
}
}
}
然后插入下面的数据:
// 示例数据
POST test/_doc
{
"title": ["Sony", "WH-1000XM3"]
}
POST test/_doc
{
"title": ["SK-II", "PITERA"]
}
POST test/_doc
{
"title": ["Nintendo", "switch"]
}
查询的DSL语句如下:
// 自动补全查询
GET /test/_search
{
"suggest": {
"title_suggest": { //名字随便起
"text": "s", // 要补全的关键字
"completion": { //补全方式
"field": "title", // 补全查询的字段
"skip_duplicates": true, // 跳过重复的
"size": 10 // 获取前10条结果
}
}
}
}
RestClient操作
准备工作
mysql结构
CREATE DATABASE heima;
USE heima;
CREATE TABLE `tb_hotel` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店id',
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店名称;例:7天酒店',
`address` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店地址;例:航头路',
`price` int(10) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店价格;例:329',
`score` int(2) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店评分;例:45,就是4.5分',
`brand` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店品牌;例:如家',
`city` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '所在城市;例:上海',
`star_name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '酒店星级,从低到高分别是:1星到5星,1钻到5钻',
`business` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商圈;例:虹桥',
`latitude` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '纬度;例:31.2497',
`longitude` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '经度;例:120.3925',
`pic` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '酒店图片;例:/img/1.jpg',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
导入工程
- 修改配置文件 --- mysql
mapping映射分析
创建索引库,最关键的是mapping映射,而mapping映射要考虑的信息包括:
- 字段名
- 字段数据类型
- 是否参与搜索
- 是否需要分词
- 分词器是什么
其中:
- 字段名、字段数据类型,可以参考数据表结构的名称和类型
- 是否参与搜索要分析业务来判断,例如图片地址,就无需参与搜索
- 是否分词呢要看内容,内容如果是一个整体就无需分词,反之则要分词
- 分词器,我们可以统一使用ik_max_word
索引库结构如下:
PUT /hotel
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"address":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price":{
"type": "integer"
},
"score":{
"type": "integer"
},
"brand":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"city":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"starName":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"business":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"location":{
"type": "geo_point"
},
"pic":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"all":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
初始化RestClient
在elasticsearch提供的API中,与elasticsearch一切交互都封装在一个名为RestHighLevelClient的类中,必须先完成这个对象的初始化,建立与elasticsearch的连接
依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId> </dependency>SpringBoot默认的ES版本与需要的不一致,所以我们需要覆盖默认的ES版本
<properties> <elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version> </properties>初始化RestHighLevelClient
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder( HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200") ));
CRUD操作
索引库的CURD
创建索引库
创建Request对象。因为是创建索引库的操作,因此Request是CreateIndexRequest
添加请求参数,其实就是DSL的JSON参数部分。因为json字符串很长,这里是定义了静态字符串常量MAPPING_TEMPLATE,让代码看起来更加优雅
发送请求,client.indices()方法的返回值是IndicesClient类型,封装了所有与索引库操作有关的方法
package cn.itcast.hotel.constants;
public class HotelConstants {
public static final String MAPPING_TEMPLATE = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"id\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"address\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"score\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"brand\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"city\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"starName\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"business\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"location\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"geo_point\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"pic\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
}
@Test
void createHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象,对应PUT /hotel
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求的参数:DSL语句
request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
删除索引库
@Test
void testDeleteHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象,对应DELETE /hotel
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发送请求
client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
判断索引库是否存在
@Test
void testExistsHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象,对应GET /hotel
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发送请求
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.输出
System.err.println(exists ? "索引库已经存在!" : "索引库不存在!");
}
文档的CRUD
索引库实体类
- 对应数据库
@Data
@TableName("tb_hotel")
public class Hotel {
@TableId(type = IdType.INPUT)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer price;
private Integer score;
private String brand;
private String city;
private String starName;
private String business;
private String longitude;
private String latitude;
private String pic;
}
- 对应索引库
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class HotelDoc {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer price;
private Integer score;
private String brand;
private String city;
private String starName;
private String business;
private String location;
private String pic;
public HotelDoc(Hotel hotel) {
this.id = hotel.getId();
this.name = hotel.getName();
this.address = hotel.getAddress();
this.price = hotel.getPrice();
this.score = hotel.getScore();
this.brand = hotel.getBrand();
this.city = hotel.getCity();
this.starName = hotel.getStarName();
this.business = hotel.getBusiness();
this.location = hotel.getLatitude() + ", " + hotel.getLongitude();
this.pic = hotel.getPic();
}
}
新增文档
创建Request对象
准备请求参数,也就是DSL中的JSON文档
发送请求
变化的地方在于,这里直接使用client.xxx()的API,不再需要client.indices()
@Test
void testAddDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.根据id查询酒店数据
Hotel hotel = hotelService.getById(61083L);
// 2.转换为文档类型
HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);
// 3.将HotelDoc转json
String json = JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc);
// 1.准备Request对象,对应POST /{索引库名}/_doc/61081
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString());
// 2.准备Json文档,对应{"name":"如家","address":"上海市",....}
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
查询文档
@Test
void testGetDocumentById() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request,对应GET /hotel/_doc/{id}
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.发送请求,得到响应
GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.解析响应结果
String json = response.getSourceAsString();
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
System.out.println(hotelDoc);
}
删除文档
@Test
void testDeleteDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request,对应DELETE /hotel/_doc/{id}
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.发送请求
client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
修改文档
- 全量修改和新增相同
- 增量修改
@Test
void testUpdateDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request,对应POST /hotel/_update/{id}
UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.准备请求参数
request.doc(
"price", "952",
"starName", "四钻"
);
// 3.发送请求
client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
批量操作
批量处理BulkRequest,有一个add(),添加请求
- IndexRequest,也就是新增
- UpdateRequest,也就是修改
- DeleteRequest,也就是删除
@Test
void testBulkRequest() throws IOException {
// 批量查询酒店数据
List<Hotel> hotels = hotelService.list();
// 1.创建Request
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
// 2.准备参数,添加多个新增的Request
for (Hotel hotel : hotels) {
// 2.1.转换为文档类型HotelDoc
HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);
// 2.2.创建新增文档的Request对象
request.add(new IndexRequest("hotel")
.id(hotelDoc.getId().toString())
.source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc), XContentType.JSON));
}
// 3.发送请求
client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
总结
JavaRestClient操作elasticsearch的流程基本类似。核心是client.indices()方法来获取索引库的操作对象。
索引库操作的基本步骤:
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxIndexRequest。XXX是Create、Get、Delete
- 准备DSL( Create时需要,其它是无参)
- 发送请求,调用RestHighLevelClient#indices().xxx()方法,xxx是create、exists、delete
文档操作的基本步骤:
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxRequest。XXX是Index、Get、Update、Delete、Bulk
- 准备参数(Index、Update、Bulk时需要)
- 发送请求。调用RestHighLevelClient#.xxx()方法,xxx是index、get、update、delete、bulk
- 解析结果(Get时需要)
搜索 & 结果处理
发起请求步骤
创建
SearchRequest对象,指定索引库名准备Request.source(),也就是DSL
- 利用_
request.source()_构建DSL,DSL中可以包含查询、分页、排序、高亮等 - 利用_
QueryBuilders_包含match、term、function_score、bool等各种查询,如matchAllQuery()构建一个match_all查询的DSL - 传入request.source() 的
query()方法
- 利用_
利用client.search()发送请求,得到响应
解析响应步骤
hits:命中的结果total:总条数,其中的value是具体的总条数值max_score:所有结果中得分最高的文档的相关性算分hits:搜索结果的文档数组,其中的每个文档都是一个json对象_source:文档中的原始数据,也是json对象
因此,我们解析响应结果,就是逐层解析JSON字符串,流程如下:
SearchHits:通过response.getHits()获取,就是JSON中的最外层的hits,代表命中的结果SearchHits#getTotalHits().value:获取总条数信息SearchHits#getHits():获取SearchHit数组,也就是文档数组SearchHit#getSourceAsString():获取文档结果中的_source,也就是原始的json文档数据
查询所有
- QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery() --- 对应 match_all
@Test
void testMatchAll() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
request.source()
.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
private void handleResponse(SearchResponse response) {
// 4.解析响应
SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits();
// 4.1.获取总条数
long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value;
System.out.println("共搜索到" + total + "条数据");
// 4.2.文档数组
SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits();
// 4.3.遍历
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
// 获取文档source
String json = hit.getSourceAsString();
// 反序列化
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
System.out.println("hotelDoc = " + hotelDoc);
}
}
全文检索
- QueryBuilders.matchQuery() --- 对应 match
- QueryBuilders.matchQuery() --- 对应 multi_match
@Test
void testMatch() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
request.source()
.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", "如家"));
//QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("如家","name","busness")
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
精确查询
- QueryBuilders.termQuery("city","杭州") --- 对应 term
- QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").gte(100).lte(150) --- 对应 range
布尔查询
- QueryBuilders.boolQuery()返回BoolQueryBuilder,添加条件 --- 对应 bool
@Test
void testBool() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.准备BooleanQuery
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// 2.2.添加term
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", "杭州"));
// 2.3.添加range
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").lte(250));
request.source().query(boolQuery);
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
算分函数查询
@Test
void testBool() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.准备BooleanQuery
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// 2.2.添加term
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", "杭州"));
// 2.3.添加range
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").lte(250));
// 2.4.准备FunctionScoreQueryBuilder
FunctionScoreQueryBuilder functionScoreQuery =
QueryBuilders.functionScoreQuery(
// 原始查询,相关性算分的查询
boolQuery,
// function score的数组
new FunctionScoreQueryBuilder.FilterFunctionBuilder[]{
// 其中的一个function score 元素
new FunctionScoreQueryBuilder.FilterFunctionBuilder(
// 过滤条件
QueryBuilders.termQuery("isAD", true),
// 算分函数
ScoreFunctionBuilders.weightFactorFunction(10)
)
});
request.source().query(functionScoreQuery);
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
排序 & 分页
@Test
void testPageAndSort() throws IOException {
// 页码,每页大小
int page = 1, size = 5;
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
// 2.2.排序 sort
request.source().sort("price", SortOrder.ASC);
// 2.3.分页 from、size
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(5);
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
地理排序
@Test
void testPageAndSort() throws IOException {
// 页码,每页大小
int page = 1, size = 5;
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
// 2.2.排序 sort
String location = "31.03463,121.61245";
request.source().sort(SortBuilders
.geoDistanceSort("location", new GeoPoint(location))
.order(SortOrder.ASC)
.unit(DistanceUnit.KILOMETERS)
);
// 2.3.分页 from、size
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(5);
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
高亮
查询的DSL:其中除了查询条件,还需要添加高亮条件,同样是与query同级
- 传入new HighlightBuilder().field("name").requireFieldMatch(false)
@Test void testHighlight() throws IOException { // 1.准备Request SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel"); // 2.准备DSL // 2.1.query request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", "如家")); // 2.2.高亮 request.source().highlighter(new HighlightBuilder().field("name").requireFieldMatch(false)); // 3.发送请求 SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 4.解析响应 handleResponse(response); }结果解析:结果除了要解析_source文档数据,还要解析高亮结果
- 第一步:从结果中获取source。hit.getSourceAsString(),这部分是非高亮结果,json字符串。还需要反序列为HotelDoc对象
- 第二步:获取高亮结果。hit.getHighlightFields(),返回值是一个Map,key是高亮字段名称,值是HighlightField对象,代表高亮值
- 第三步:从map中根据高亮字段名称,获取高亮字段值对象HighlightField
- 第四步:从HighlightField中获取Fragments,并且转为字符串。这部分就是真正的高亮字符串了
- 第五步:用高亮的结果替换HotelDoc中的非高亮结果
private void handleResponse(SearchResponse response) { // 4.解析响应 SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits(); // 4.1.获取总条数 long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value; System.out.println("共搜索到" + total + "条数据"); // 4.2.文档数组 SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits(); // 4.3.遍历 for (SearchHit hit : hits) { // 获取文档source String json = hit.getSourceAsString(); // 反序列化 HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class); // 获取高亮结果 Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields(); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(highlightFields)) { // 根据字段名获取高亮结果 HighlightField highlightField = highlightFields.get("name"); if (highlightField != null) { // 获取高亮值 String name = highlightField.getFragments()[0].string(); // 覆盖非高亮结果 hotelDoc.setName(name); } } System.out.println("hotelDoc = " + hotelDoc); } }
数据聚合
- 聚合条件与query条件同级别,因此需要使用request.source()来指定聚合条件
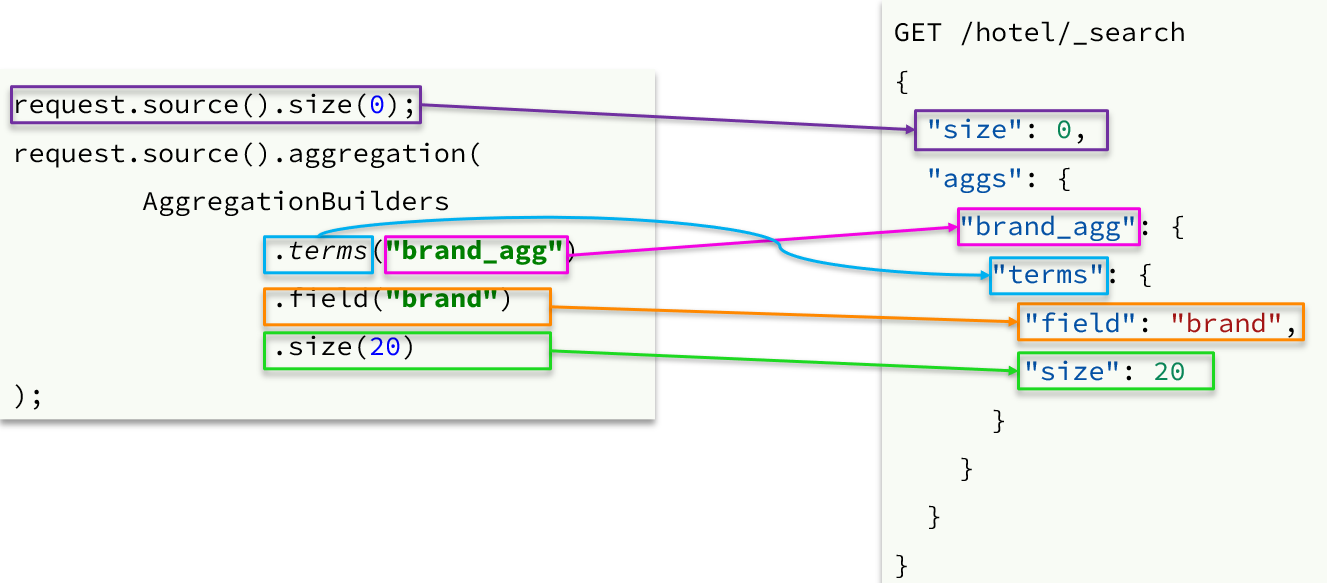
聚合的结果也与查询结果不同,API也比较特殊。不过同样是JSON逐层解析
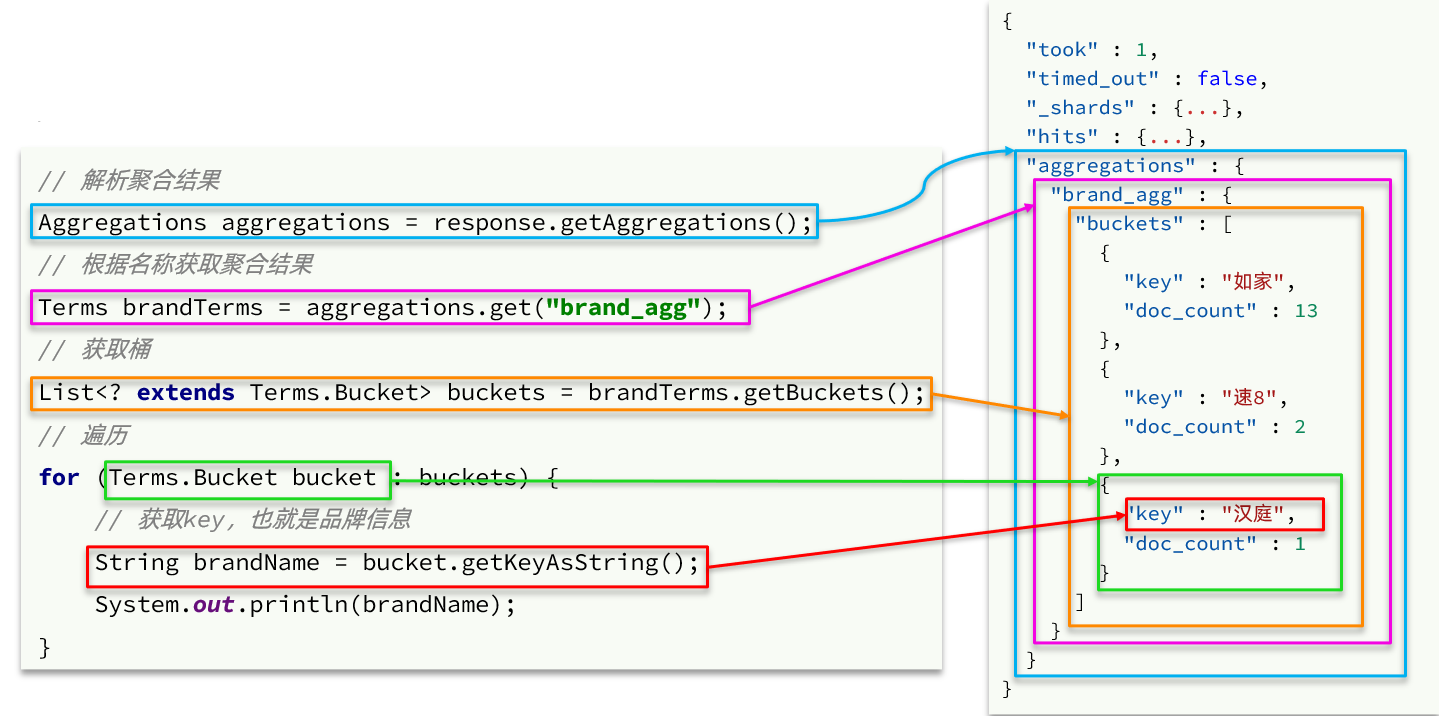
image-20221007232952649
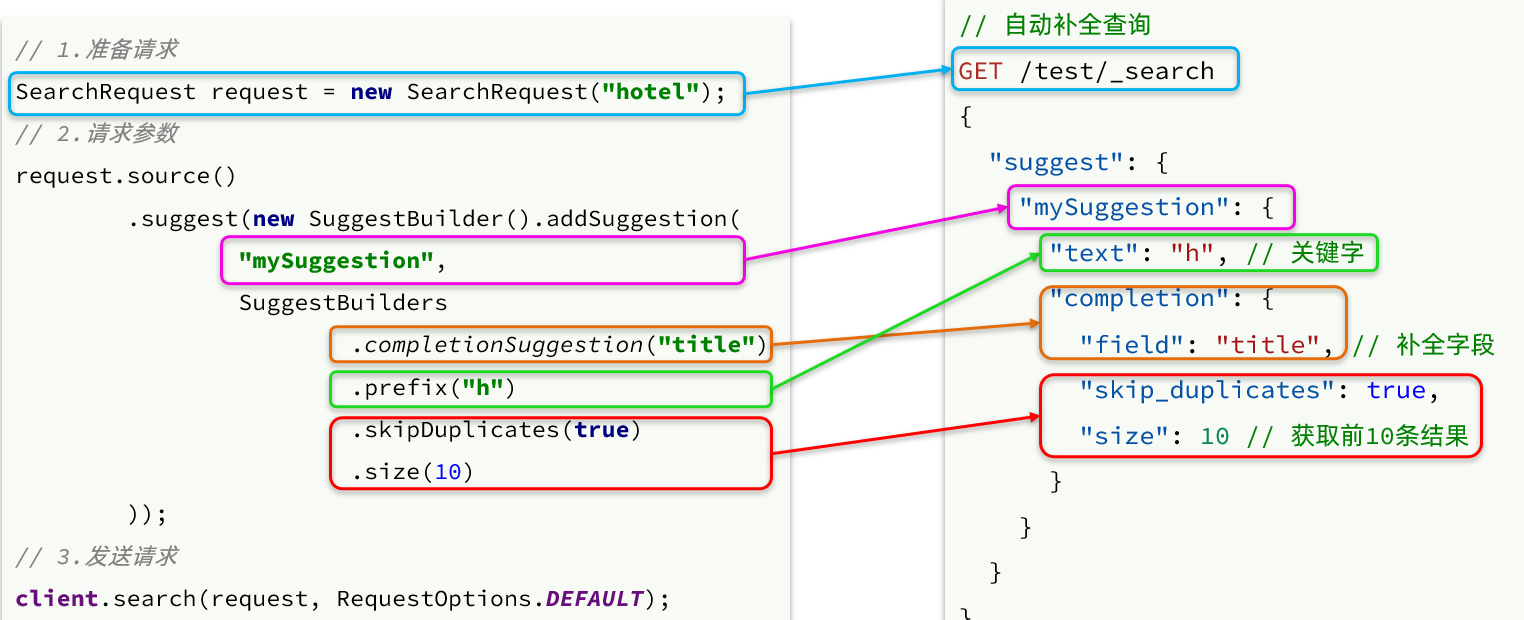
自动补全
- 请求
解析
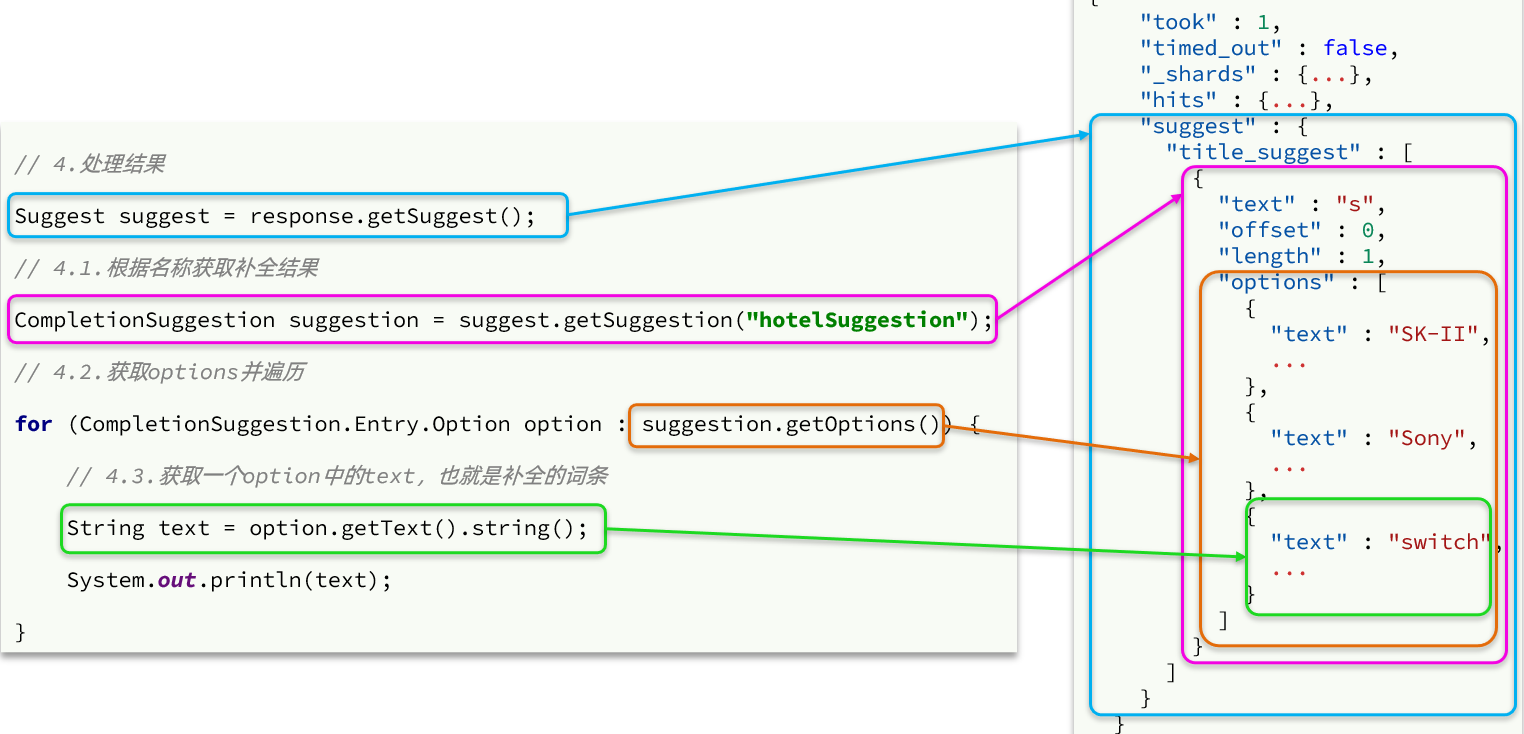
image-20221007235135822
案例
准备工作
数据库、索引库映射
PUT /hotel { "mappings": { "properties": { "id": { "type": "keyword" }, "name":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "copy_to": "all" }, "address":{ "type": "keyword", "index": false }, "price":{ "type": "integer" }, "score":{ "type": "integer" }, "brand":{ "type": "keyword", "copy_to": "all" }, "city":{ "type": "keyword", "copy_to": "all" }, "starName":{ "type": "keyword" }, "business":{ "type": "keyword" }, "location":{ "type": "geo_point" }, "pic":{ "type": "keyword", "index": false }, "all":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } } }依赖
<elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version> <!--FastJson--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.71</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId> </dependency>配置文件
mysql
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/heima?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&rewriteBatchedStatements=true username: root password: root driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driverserver.port:
启动类
@MapperScan("cn.itcast.hotel.mapper") @SpringBootApplication public class HotelDemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(HotelDemoApplication.class, args); } @Bean public RestHighLevelClient client(){ return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder( HttpHost.create("http://192.168.10.109:9200") )); } }同步数据库数据
@SpringBootTest class HotelDemoApplicationTests { @Autowired private RestHighLevelClient client; @Autowired private IHotelService hotelService; @Test void contextLoads() { } @Test void testBulkRequest() throws IOException { // 查询所有的酒店数据 List<Hotel> list = hotelService.list(); // 1.准备Request BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest(); // 2.准备参数 for (Hotel hotel : list) { // 2.1.转为HotelDoc HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel); // 2.2.转json String json = JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc); // 2.3.添加请求 request.add(new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotel.getId().toString()).source(json, XContentType.JSON)); } // 3.发送请求 client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } @AfterEach void tearDown() throws IOException { client.close(); } }
大搜索框
需求分析
请求方式:POST
请求路径:/hotel/list
请求参数:JSON对象,包含4个字段:
- key:搜索关键字
- page:页码
- size:每页大小
- sortBy:排序,目前暂不实现
返回值:分页查询,需要返回分页结果PageResult,包含两个属性:
total:总条数List<HotelDoc>:当前页的数据
实现业务的流程如下
- 步骤一:定义实体类,接收请求参数的JSON对象
- 步骤二:编写controller,接收页面的请求
- 步骤三:编写业务实现,利用RestHighLevelClient实现搜索、分页
pojo
前端请求参数
{ "key": "搜索关键字", "page": 1, "size": 3, "sortBy": "default" }请求参数类
@Data public class RequestParams { private String key; private Integer page; private Integer size; private String sortBy; }返回值
@Data public class PageResult { private Long total; private List<HotelDoc> hotels; public PageResult() { } public PageResult(Long total, List<HotelDoc> hotels) { this.total = total; this.hotels = hotels; } }
controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hotel")
public class HotelController {
@Autowired
private IHotelService hotelService;
// 搜索酒店数据
@PostMapping("/list")
public PageResult search(@RequestBody RequestParams params){
return hotelService.search(params);
}
}
service
public interface IHotelService{
/**
* 根据关键字搜索酒店信息
* @param params 请求参数对象,包含用户输入的关键字
* @return 酒店文档列表
*/
PageResult search(RequestParams params);
}
public class IHotelServiceImpl implements IHotelService{
@Override
public PageResult search(RequestParams params) {
try {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
String key = params.getKey();
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
if (key == null || "".equals(key)) {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
} else {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", key));
}
request.source().query(boolQuery);
// 2.2.分页
int page = params.getPage();
int size = params.getSize();
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(size);
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
return handleResponse(response);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 结果解析
private PageResult handleResponse(SearchResponse response) {
// 4.解析响应
SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits();
// 4.1.获取总条数
long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value;
// 4.2.文档数组
SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits();
// 4.3.遍历
List<HotelDoc> hotels = new ArrayList<>();
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
// 获取文档source
String json = hit.getSourceAsString();
// 反序列化
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
// 放入集合
hotels.add(hotelDoc);
}
// 4.4.封装返回
return new PageResult(total, hotels);
}
}
标签过滤
需求分析
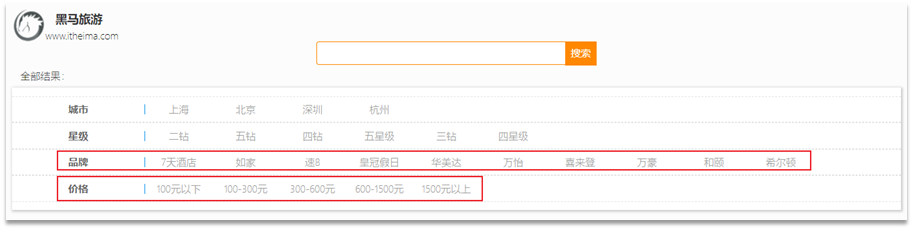
包含的过滤条件有:
- brand:品牌值
- city:城市
- minPrice~maxPrice:价格范围
- starName:星级
我们需要做两件事情:
- 修改请求参数的对象RequestParams,接收上述参数
- 修改业务逻辑,在搜索条件之外,添加一些过滤条件
修改pojo
@Data
public class RequestParams {
private String key;
private Integer page;
private Integer size;
private String sortBy;
// 下面是新增的过滤条件参数
private String city;
private String brand;
private String starName;
private Integer minPrice;
private Integer maxPrice;
}
修改service
search方法中,只有一个地方需要修改:requet.source().query( ... )其中的查询条件。
在之前的业务中,只有match查询,根据关键字搜索,现在要添加条件过滤,包括:
- 品牌过滤:是keyword类型,用term查询
- 星级过滤:是keyword类型,用term查询
- 价格过滤:是数值类型,用range查询
- 城市过滤:是keyword类型,用term查询
多个查询条件组合,肯定是boolean查询来组合:
- 关键字搜索放到must中,参与算分
- 其它过滤条件放到filter中,不参与算分
@Override
public PageResult search(RequestParams params) {
try {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
//查询
buildBoolQuery(params,request);
//分页
int page = params.getPage();
int size = params.getSize();
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(size);
//发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//解析响应
return handleResponse(response);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private void buildBoolQuery(RequestParams params, SearchRequest request) {
// 构建BoolQueryBuilder
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// 关键字查询
String key = params.getKey();
if (key == null || "".equals(key)) {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
} else {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", key));
}
//城市查询
String city = params.getCity();
if (city != null && !"".equals(city)){
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", city));
}
//品牌查询
String brand = params.getBrand();
if (brand != null && !"".equals(brand)){
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("brand", brand));
}
//星级查询
String starName = params.getStarName();
if (starName != null && !"".equals(starName)){
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("starName",starName));
}
//价格查询
Integer minPrice = params.getMinPrice();
Integer maxPrice = params.getMaxPrice();
if (minPrice != null && maxPrice != null){
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price")
.gte(minPrice)
.lte(maxPrice));
}
request.source().query(boolQuery);
}
附近的酒店
需求分析
{
"key": "搜索关键字",
"location": "31.03463,121.61245",
"page": 1,
"size": 3,
"sortBy": "default"
}
我们要做的事情就是基于这个location坐标,然后按照距离对周围酒店排序。实现思路如下:
- 修改RequestParams参数,接收location字段
- 修改search方法业务逻辑,如果location有值,添加根据geo_distance排序的功能
修改pojo
@Data
public class RequestParams {
private String key;
private Integer page;
private Integer size;
private String sortBy;
private String city;
private String brand;
private String starName;
private Integer minPrice;
private Integer maxPrice;
// 我当前的地理坐标
private String location;
}
修改service
@Override
public PageResult search(RequestParams params) {
try {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
buildBasicQuery(params, request);
// 2.2.分页
int page = params.getPage();
int size = params.getSize();
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(size);
// 2.3.排序
String location = params.getLocation();
if (location != null && !location.equals("")) {
request.source().sort(SortBuilders
.geoDistanceSort("location", new GeoPoint(location))
.order(SortOrder.ASC)
.unit(DistanceUnit.KILOMETERS)
);
}
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
return handleResponse(response);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
返回排序距离
修改HotelDoc类,添加距离字段
@Data @NoArgsConstructor public class HotelDoc { private Long id; private String name; private String address; private Integer price; private Integer score; private String brand; private String city; private String starName; private String business; private String location; private String pic; // 排序时的 距离值 private Object distance; public HotelDoc(Hotel hotel) { this.id = hotel.getId(); this.name = hotel.getName(); this.address = hotel.getAddress(); this.price = hotel.getPrice(); this.score = hotel.getScore(); this.brand = hotel.getBrand(); this.city = hotel.getCity(); this.starName = hotel.getStarName(); this.business = hotel.getBusiness(); this.location = hotel.getLatitude() + ", " + hotel.getLongitude(); this.pic = hotel.getPic(); } }修改service
private PageResult handleResponse(SearchResponse response) { // 4.解析响应 SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits(); // 4.1.获取总条数 long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value; // 4.2.文档数组 SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits(); // 4.3.遍历 List<HotelDoc> hotels = new ArrayList<>(); for (SearchHit hit : hits) { // 获取文档source String json = hit.getSourceAsString(); // 反序列化 HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class); // 获取排序值 Object[] sortValues = hit.getSortValues(); if(sortvalues.length > 0){ Object sortValue = sortValue[0]; hotelDoc.setDistance(sortValue); } // 放入集合 hotels.add(hotelDoc); } // 4.4.封装返回 return new PageResult(total, hotels); }
竞价排名
需求分析
让指定酒店排名靠前。因此我们需要给这些酒店添加一个标记,这样在过滤条件中就可以根据这个标记来判断,是否要提高算分。
比如,我们给酒店添加一个字段:isAD,Boolean类型:
- true:是广告
- false:不是广告
这样function_score包含3个要素就很好确定了:
- 过滤条件:判断isAD 是否为true
- 算分函数:我们可以用最简单暴力的weight,固定加权值
- 加权方式:可以用默认的相乘,大大提高算分
业务的实现步骤包括:
给HotelDoc类添加isAD字段,Boolean类型
挑选几个你喜欢的酒店,给它的文档数据添加isAD字段,值为true
修改search方法,添加function score功能,给isAD值为true的酒店增加权重
修改HotelDoc
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class HotelDoc {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer price;
private Integer score;
private String brand;
private String city;
private String starName;
private String business;
private String location;
private String pic;
// 排序时的 距离值
private Object distance;
//广告标记
private Boolean isAD;
public HotelDoc(Hotel hotel) {
this.id = hotel.getId();
this.name = hotel.getName();
this.address = hotel.getAddress();
this.price = hotel.getPrice();
this.score = hotel.getScore();
this.brand = hotel.getBrand();
this.city = hotel.getCity();
this.starName = hotel.getStarName();
this.business = hotel.getBusiness();
this.location = hotel.getLatitude() + ", " + hotel.getLongitude();
this.pic = hotel.getPic();
}
}
索引库添加广告标记
POST /hotel/_update/1902197537
{
"doc": {
"isAD": true
}
}
POST /hotel/_update/2056126831
{
"doc": {
"isAD": true
}
}
POST /hotel/_update/1989806195
{
"doc": {
"isAD": true
}
}
POST /hotel/_update/2056105938
{
"doc": {
"isAD": true
}
}
添加算分函数查询
接下来我们就要修改查询条件了。之前是用的boolean 查询,现在要改成function_socre查询
private void buildBasicQuery(RequestParams params, SearchRequest request) {
// 1.构建BooleanQuery
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// 关键字搜索
String key = params.getKey();
if (key == null || "".equals(key)) {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
} else {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", key));
}
// 城市条件
if (params.getCity() != null && !params.getCity().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", params.getCity()));
}
// 品牌条件
if (params.getBrand() != null && !params.getBrand().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("brand", params.getBrand()));
}
// 星级条件
if (params.getStarName() != null && !params.getStarName().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("starName", params.getStarName()));
}
// 价格
if (params.getMinPrice() != null && params.getMaxPrice() != null) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders
.rangeQuery("price")
.gte(params.getMinPrice())
.lte(params.getMaxPrice())
);
}
// 2.算分控制
FunctionScoreQueryBuilder functionScoreQuery =
QueryBuilders.functionScoreQuery(
// 原始查询,相关性算分的查询
boolQuery,
// function score的数组
new FunctionScoreQueryBuilder.FilterFunctionBuilder[]{
// 其中的一个function score 元素
new FunctionScoreQueryBuilder.FilterFunctionBuilder(
// 过滤条件
QueryBuilders.termQuery("isAD", true),
// 算分函数
ScoreFunctionBuilders.weightFactorFunction(10)
)
});
request.source().query(functionScoreQuery);
}
动态标签
业务需求
需求:搜索页面的品牌、城市等信息不应该是在页面写死,而是通过聚合索引库中的酒店数据得来的
image-20221007233331658 分析
- 使用聚合功能,利用Bucket聚合,对搜索结果中的文档基于品牌分组、基于城市分组,就能得知包含哪些品牌、哪些城市了
- 因为是对搜索结果聚合,因此聚合是限定范围的聚合,也就是说聚合的限定条件跟搜索文档的条件一致
- 请求参数与搜索文档的参数完全一致
- 返回值Map结构
- key是字符串,城市、星级、品牌、价格
- value是集合,例如多个城市的名称
controller
@PostMapping("filters")
public Map<String, List<String>> getFilters(@RequestBody RequestParams params){
return hotelService.getFilters(params);
}
service
Map<String, List<String>> filters(RequestParams params);
@Override
public Map<String, List<String>> filters(RequestParams params) {
try {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
buildBasicQuery(params, request);
// 2.2.设置size
request.source().size(0);
// 2.3.聚合
buildAggregation(request);
// 3.发出请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析结果
Map<String, List<String>> result = new HashMap<>();
Aggregations aggregations = response.getAggregations();
// 4.1.根据品牌名称,获取品牌结果
List<String> brandList = getAggByName(aggregations, "brandAgg");
result.put("品牌", brandList);
// 4.2.根据品牌名称,获取品牌结果
List<String> cityList = getAggByName(aggregations, "cityAgg");
result.put("城市", cityList);
// 4.3.根据品牌名称,获取品牌结果
List<String> starList = getAggByName(aggregations, "starAgg");
result.put("星级", starList);
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private void buildAggregation(SearchRequest request) {
request.source().aggregation(AggregationBuilders
.terms("brandAgg")
.field("brand")
.size(100)
);
request.source().aggregation(AggregationBuilders
.terms("cityAgg")
.field("city")
.size(100)
);
request.source().aggregation(AggregationBuilders
.terms("starAgg")
.field("starName")
.size(100)
);
}
private List<String> getAggByName(Aggregations aggregations, String aggName) {
// 4.1.根据聚合名称获取聚合结果
Terms brandTerms = aggregations.get(aggName);
// 4.2.获取buckets
List<? extends Terms.Bucket> buckets = brandTerms.getBuckets();
// 4.3.遍历
List<String> brandList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Terms.Bucket bucket : buckets) {
// 4.4.获取key
String key = bucket.getKeyAsString();
brandList.add(key);
}
return brandList;
}
自动补全
业务需求
- 当用户在搜索框输入字符时,我们应该提示出与该字符有关的搜索项
因为需要根据拼音字母来推断,因此要用到拼音分词功能
需要修改索引库中的配置。但是我们知道索引库是无法修改的,只能删除然后重新创建。
需要添加一个字段,用来做自动补全,将brand、suggestion、city等都放进去,作为自动补全的提示
步骤
修改hotel索引库结构,设置自定义拼音分词器
修改索引库的name、all字段,使用自定义分词器
索引库添加一个新字段suggestion,类型为completion类型,使用自定义的分词器
给HotelDoc类添加suggestion字段,内容包含brand、business
重新导入数据到hotel库
重新创建索引库
// 酒店数据索引库
PUT /hotel
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"text_anlyzer": {
"tokenizer": "ik_max_word",
"filter": "py"
},
"completion_analyzer": {
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"filter": "py"
}
},
"filter": {
"py": {
"type": "pinyin",
"keep_full_pinyin": false,
"keep_joined_full_pinyin": true,
"keep_original": true,
"limit_first_letter_length": 16,
"remove_duplicated_term": true,
"none_chinese_pinyin_tokenize": false
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "text_anlyzer",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"address":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price":{
"type": "integer"
},
"score":{
"type": "integer"
},
"brand":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"city":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"starName":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"business":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"location":{
"type": "geo_point"
},
"pic":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"all":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "text_anlyzer",
"search_analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"suggestion":{
"type": "completion",
"analyzer": "completion_analyzer"
}
}
}
}
导入数据:略
修改HotelDoc
HotelDoc中要添加一个字段,用来做自动补全,内容可以是酒店品牌、城市、商圈等信息。按照自动补全字段的要求,最好是这些字段的数组。
因此我们在HotelDoc中添加一个suggestion字段,类型为List<String>,然后将brand、city、business等信息放到里面。
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class HotelDoc {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer price;
private Integer score;
private String brand;
private String city;
private String starName;
private String business;
private String location;
private String pic;
private Object distance;
private Boolean isAD;
private List<String> suggestion;
public HotelDoc(Hotel hotel) {
this.id = hotel.getId();
this.name = hotel.getName();
this.address = hotel.getAddress();
this.price = hotel.getPrice();
this.score = hotel.getScore();
this.brand = hotel.getBrand();
this.city = hotel.getCity();
this.starName = hotel.getStarName();
this.business = hotel.getBusiness();
this.location = hotel.getLatitude() + ", " + hotel.getLongitude();
this.pic = hotel.getPic();
// 组装suggestion
if(this.business.contains("/")){
// business有多个值,需要切割
String[] arr = this.business.split("/");
// 添加元素
this.suggestion = new ArrayList<>();
this.suggestion.add(this.brand);
Collections.addAll(this.suggestion, arr);
}else {
this.suggestion = Arrays.asList(this.brand, this.business);
}
}
}
controller
返回值是补全词条的集合,类型为List<String>
@GetMapping("suggestion")
public List<String> getSuggestions(@RequestParam("key") String prefix) {
return hotelService.getSuggestions(prefix);
}
service
List<String> getSuggestions(String prefix);
@Override
public List<String> getSuggestions(String prefix) {
try {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
request.source().suggest(new SuggestBuilder().addSuggestion(
"suggestions",
SuggestBuilders.completionSuggestion("suggestion")
.prefix(prefix)
.skipDuplicates(true)
.size(10)
));
// 3.发起请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析结果
Suggest suggest = response.getSuggest();
// 4.1.根据补全查询名称,获取补全结果
CompletionSuggestion suggestions = suggest.getSuggestion("suggestions");
// 4.2.获取options
List<CompletionSuggestion.Entry.Option> options = suggestions.getOptions();
// 4.3.遍历
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(options.size());
for (CompletionSuggestion.Entry.Option option : options) {
String text = option.getText().toString();
list.add(text);
}
return list;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
数据同步
数据同步:数据来自于mysql数据库,因此mysql数据发生改变时,elasticsearch也必须跟着改变
解决方案
同步调用
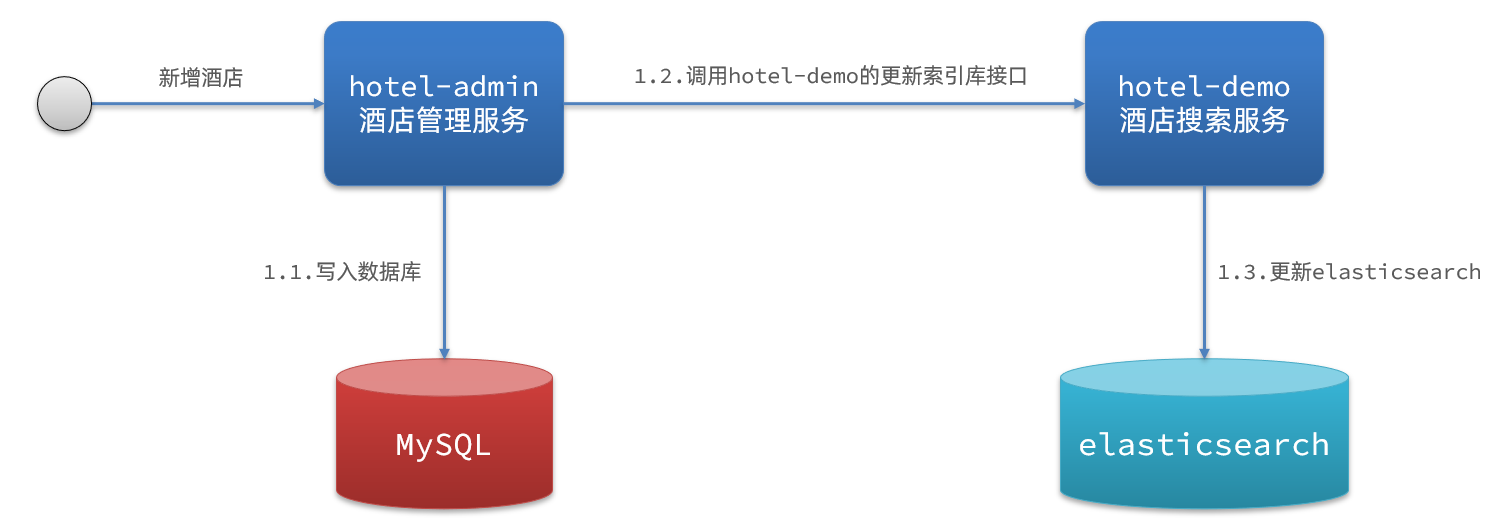
基本步骤如下:
- hotel-demo对外提供接口,用来修改elasticsearch中的数据
- 酒店管理服务在完成数据库操作后,直接调用hotel-demo提供的接口
异步通知

流程如下:
- hotel-admin对mysql数据库数据完成增、删、改后,发送MQ消息
- hotel-demo监听MQ,接收到消息后完成elasticsearch数据修改
监听binlog
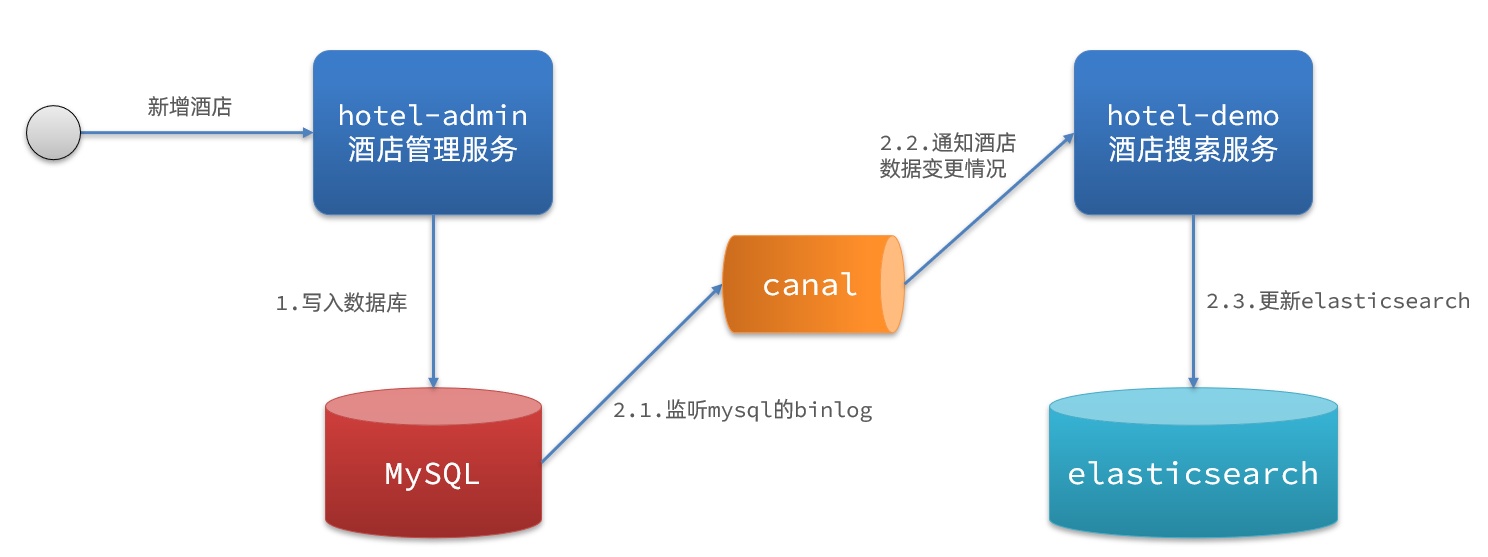
流程如下:
- 给mysql开启binlog功能
- mysql完成增、删、改操作都会记录在binlog中
- hotel-demo基于canal监听binlog变化,实时更新elasticsearch中的内容
选择
方式一:同步调用
- 优点:实现简单,粗暴
- 缺点:业务耦合度高
方式二:异步通知
- 优点:低耦合,实现难度一般
- 缺点:依赖mq的可靠性
方式三:监听binlog
- 优点:完全解除服务间耦合
- 缺点:开启binlog增加数据库负担、实现复杂度高
MQ实现数据同步
Rocketmq实现数据同步
操作数据库的服务为消息提供者,当数据发生增删改时,发送消息
操作索引库的服务为消息消费者,当数据发生增删改时,接收消息
引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.rocketmq</groupId> <artifactId>rocketmq-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.0.3</version> </dependency>配置文件
rocketmq: name-server: 192.168.10.103:9876;192.168.10.102:9876发送消息
@RestController @RequestMapping("hotel") public class HotelController { @Autowired private IHotelService hotelService; @Autowired private RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate; //@GetMapping("/{id}") //...... @PostMapping public void saveHotel(@RequestBody Hotel hotel){ hotelService.save(hotel); rocketMQTemplate.convertAndSend("insert-hotel",hotel.getId()); } @PutMapping() public void updateById(@RequestBody Hotel hotel){ if (hotel.getId() == null) { throw new InvalidParameterException("id不能为空"); } hotelService.updateById(hotel); rocketMQTemplate.convertAndSend("insert-hotel",hotel.getId()); } @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public void deleteById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) { hotelService.removeById(id); rocketMQTemplate.convertAndSend("delete-hotel",id); } }接收消息
- 监听器
package cn.itcast.hotel.mq; @RocketMQMessageListener(topic = "delete-hotel", consumerGroup = "hotel-consumer1") @Service public class HotelDelete implements RocketMQListener<Long> { @Autowired private IHotelService hotelService; @Override public void onMessage(Long id) { System.out.println("开始同步"); hotelService.deleteById(id); System.out.println("同步完成"); } }package cn.itcast.hotel.mq; @RocketMQMessageListener(topic = "insert-hotel", consumerGroup = "hotel-consumer2") @Service public class HotelInsertOrUpdate implements RocketMQListener<Long> { @Autowired private IHotelService hotelService; @Override public void onMessage(Long id) { System.out.println("开始同步"); hotelService.insertById(id); System.out.println("同步完成"); } }service
public interface IHotelService extends IService<Hotel> { PageResult search(RequestParams params); Map<String, List<String>> getFilters(RequestParams params); List<String> getSuggestions(String prefix); void deleteById(Long id); void insertById(Long id); }@Override public void deleteById(Long id) { DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("hotel", id.toString()); try { client.delete(deleteRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void insertById(Long id) { Hotel hotel = getById(id); HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel); IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotel.getId().toString()); indexRequest.source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc), XContentType.JSON); try { client.index(indexRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }
Rabbitmq实现数据同步
依赖
<!--amqp--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>常量类
package cn.itcast.hotel.constatnts; public class MqConstants { /** * 交换机 */ public final static String HOTEL_EXCHANGE = "hotel.topic"; /** * 监听新增和修改的队列 */ public final static String HOTEL_INSERT_QUEUE = "hotel.insert.queue"; /** * 监听删除的队列 */ public final static String HOTEL_DELETE_QUEUE = "hotel.delete.queue"; /** * 新增或修改的RoutingKey */ public final static String HOTEL_INSERT_KEY = "hotel.insert"; /** * 删除的RoutingKey */ public final static String HOTEL_DELETE_KEY = "hotel.delete"; }配置类,声明队列、交换机
@Configuration public class MqConfig { @Bean public TopicExchange topicExchange(){ return new TopicExchange(MqConstants.HOTEL_EXCHANGE, true, false); } @Bean public Queue insertQueue(){ return new Queue(MqConstants.HOTEL_INSERT_QUEUE, true); } @Bean public Queue deleteQueue(){ return new Queue(MqConstants.HOTEL_DELETE_QUEUE, true); } @Bean public Binding insertQueueBinding(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(insertQueue()).to(topicExchange()).with(MqConstants.HOTEL_INSERT_KEY); } @Bean public Binding deleteQueueBinding(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(deleteQueue()).to(topicExchange()).with(MqConstants.HOTEL_DELETE_KEY); } }发送
image-20221010001217621 接收
@Component public class HotelListener { @Autowired private IHotelService hotelService; /** * 监听酒店新增或修改的业务 * @param id 酒店id */ @RabbitListener(queues = MqConstants.HOTEL_INSERT_QUEUE) public void listenHotelInsertOrUpdate(Long id){ hotelService.insertById(id); } /** * 监听酒店删除的业务 * @param id 酒店id */ @RabbitListener(queues = MqConstants.HOTEL_DELETE_QUEUE) public void listenHotelDelete(Long id){ hotelService.deleteById(id); } }service同
集群
单机的elasticsearch做数据存储,必然面临两个问题:海量数据存储问题、单点故障问题。
- 海量数据存储问题:将索引库从逻辑上拆分为N个分片(shard),存储到多个节点
- 单点故障问题:将分片数据在不同节点备份(replica )
ES集群相关概念:
集群(cluster):一组拥有共同的 cluster name 的 节点。
- :集群中的一个 Elasticearch 实例
- :索引可以被拆分为不同的部分进行存储,称为分片。在集群环境下,一个索引的不同分片可以拆分到不同的节点中
解决问题:数据量太大,单点存储量有限的问题
主分片(Primary shard):相对于副本分片的定义
副本分片(Replica shard)每个主分片可以有一个或者多个副本,数据和主分片一样
数据备份可以保证高可用,但是每个分片备份一份,所需要的节点数量就会翻一倍,成本实在是太高了!
为了在高可用和成本间寻求平衡,我们可以这样做:
- 首先对数据分片,存储到不同节点
- 然后对每个分片进行备份,放到对方节点,完成互相备份
这样可以大大减少所需要的服务节点数量,如图,我们以3分片,每个分片备份一份为例:
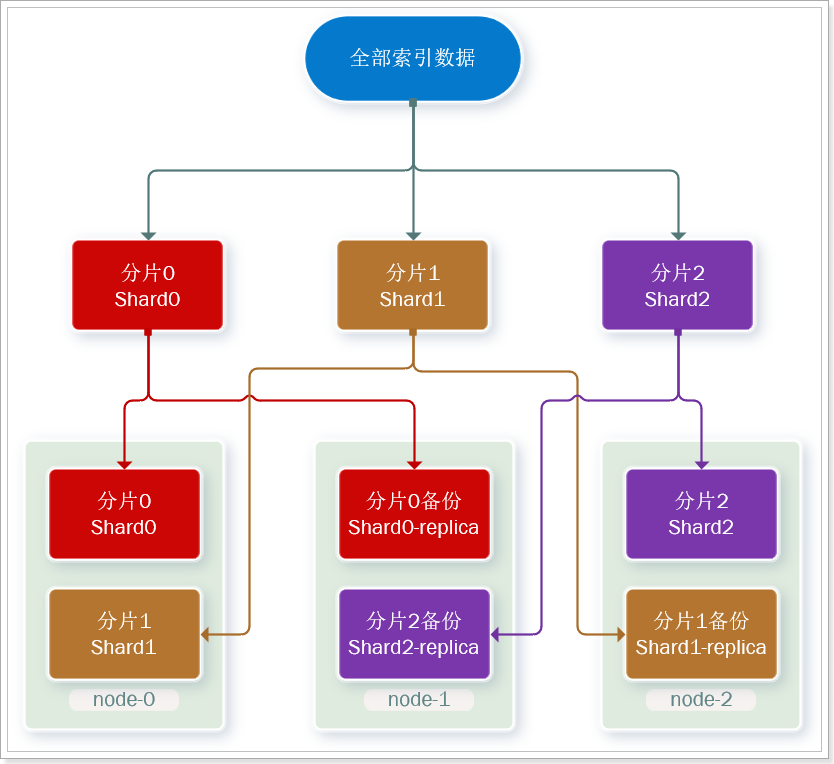
现在,每个分片都有1个备份,存储在3个节点:
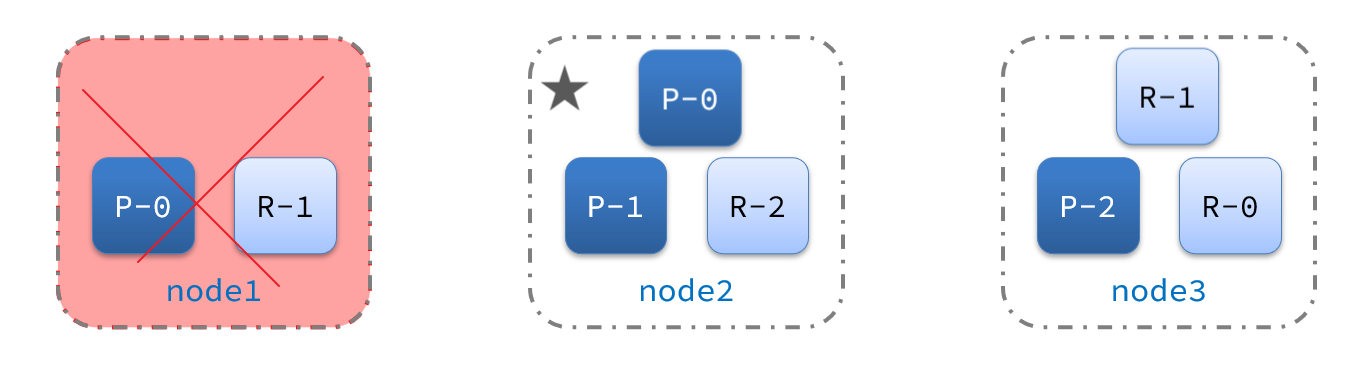
- node0:保存了分片0和1
- node1:保存了分片0和2
- node2:保存了分片1和2
创建索引库
kibana创建索引库
在DevTools中输入指令:
PUT /itcast { "settings": { "number_of_shards": 3, // 分片数量 "number_of_replicas": 1 // 副本数量 }, "mappings": { "properties": { // mapping映射定义 ... } } }
cerebro创建索引库
- 创建
填写
image-20221007231425360
查看分片效果
回到首页,即可查看索引库分片效果
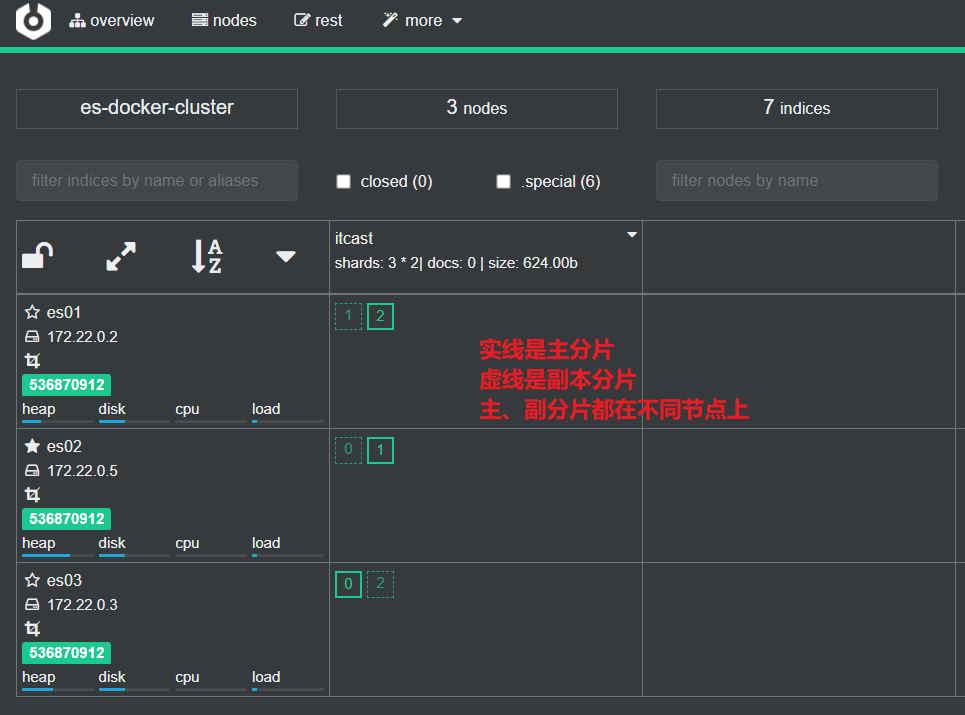
image-20221007231605228
集群脑裂
职责划分
elasticsearch中集群节点有不同的职责划分:
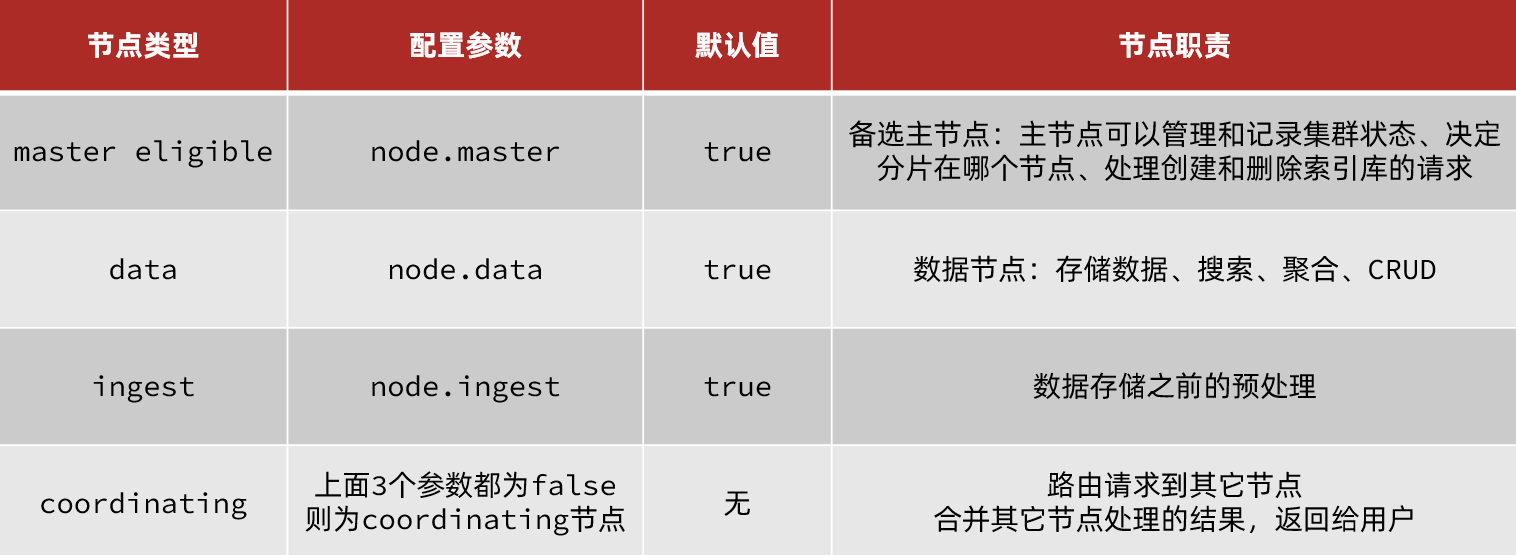
默认情况下,集群中的任何一个节点都同时具备上述四种角色。
但是真实的集群一定要将集群职责分离:
- master节点:对CPU要求高,但是内存要求第
- data节点:对CPU和内存要求都高
- coordinating节点:对网络带宽、CPU要求高
职责分离可以让我们根据不同节点的需求分配不同的硬件去部署。而且避免业务之间的互相干扰。
一个典型的es集群职责划分如图:
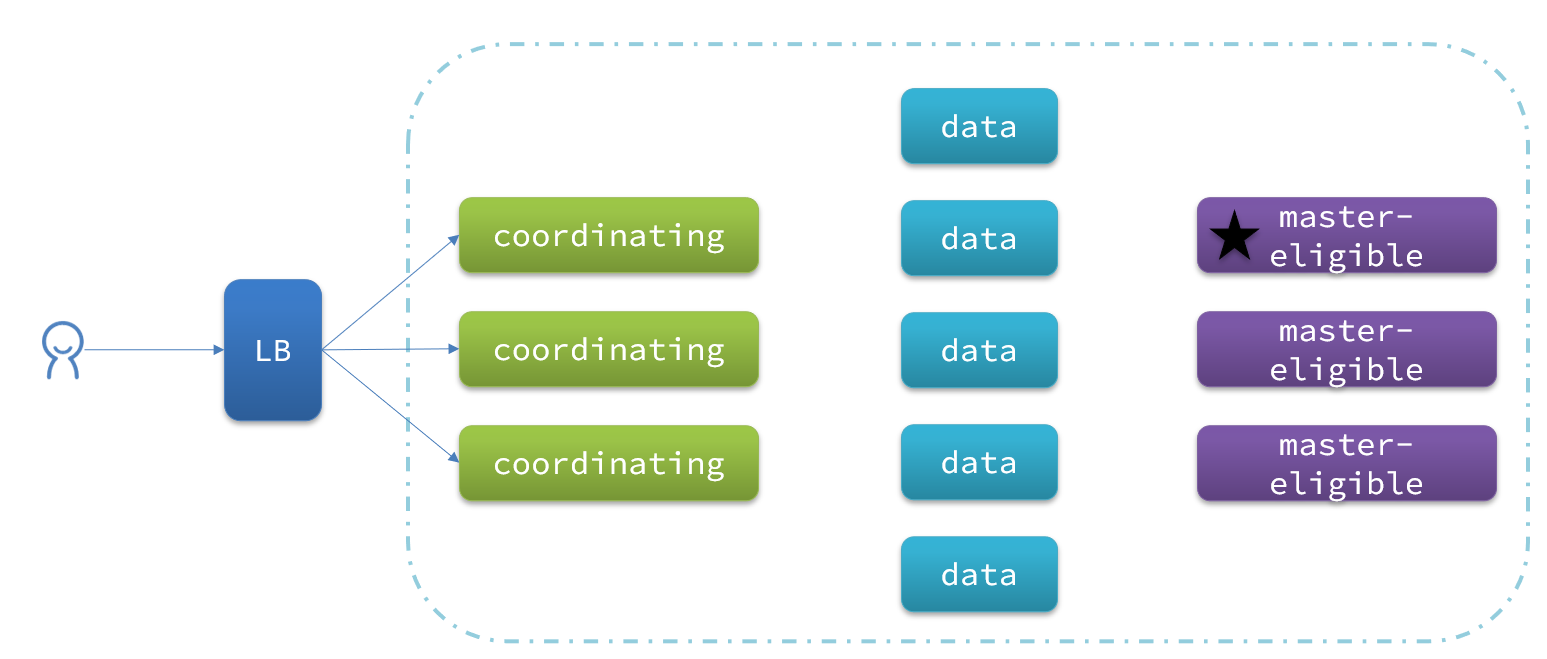
脑裂问题
脑裂是因为集群中的节点失联导致的。
例如一个集群中,主节点与其它节点失联:
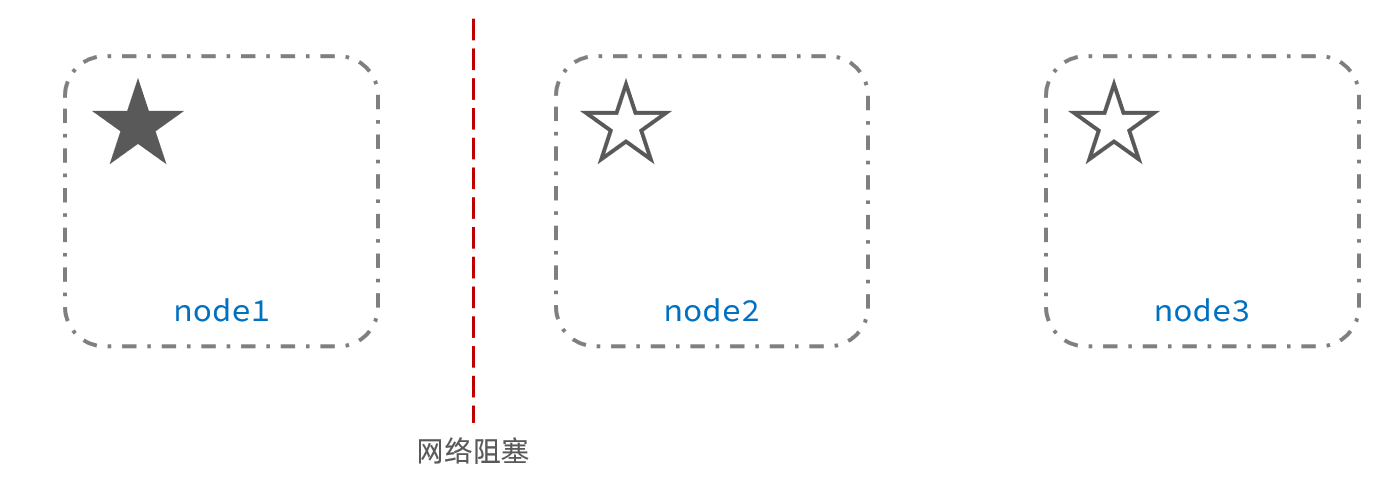
此时,node2和node3认为node1宕机,就会重新选主:
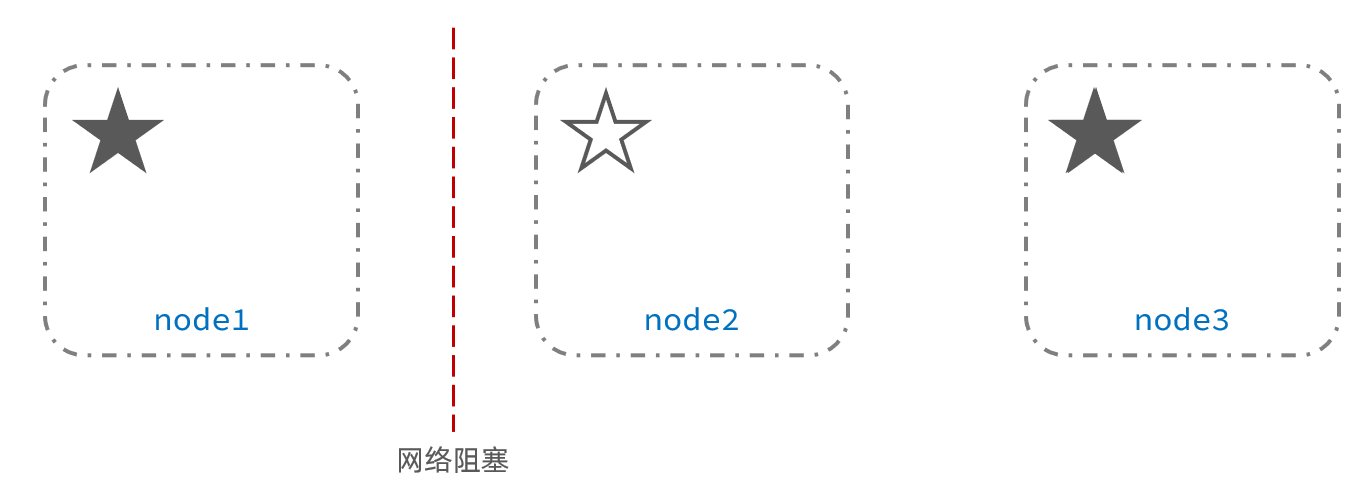
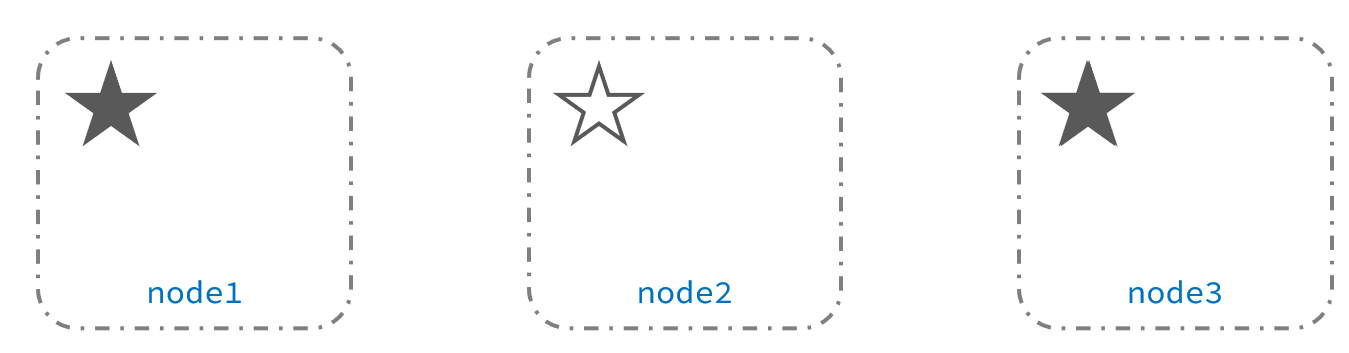
当node3当选后,集群继续对外提供服务,node2和node3自成集群,node1自成集群,两个集群数据不同步,出现数据差异。
当网络恢复后,因为集群中有两个master节点,集群状态的不一致,出现脑裂的情况:
解决脑裂的方案是,要求选票超过 ( eligible节点数量 + 1 )/ 2 才能当选为主,因此eligible节点数量最好是奇数。对应配置项是discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes,在es7.0以后,已经成为默认配置,因此一般不会发生脑裂问题
例如:3个节点形成的集群,选票必须超过 (3 + 1) / 2 ,也就是2票。node3得到node2和node3的选票,当选为主。node1只有自己1票,没有当选。集群中依然只有1个主节点,没有出现脑裂。
小结
master eligible节点的作用是什么?
- 参与集群选主
- 主节点可以管理集群状态、管理分片信息、处理创建和删除索引库的请求
data节点的作用是什么?
- 数据的CRUD
coordinator节点的作用是什么?
路由请求到其它节点
合并查询到的结果,返回给用户
分布式存储
插入三条数据:
POST /test/_doc/1
{
"title":"试着插入一条,id = 1"
}
POST /test/_doc/3
{
"title":"试着插入一条,id = 3"
}
POST /test/_doc/5
{
"title":"试着插入一条,id = 5"
}
查询:
GET /test/test/_search
结果:
分片存储原理
elasticsearch会通过hash算法来计算文档应该存储到哪个分片:
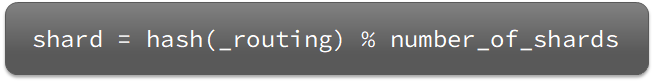
说明:
- _routing默认是文档的id
- 算法与分片数量有关,因此索引库一旦创建,分片数量不能修改!
新增文档的流程如下: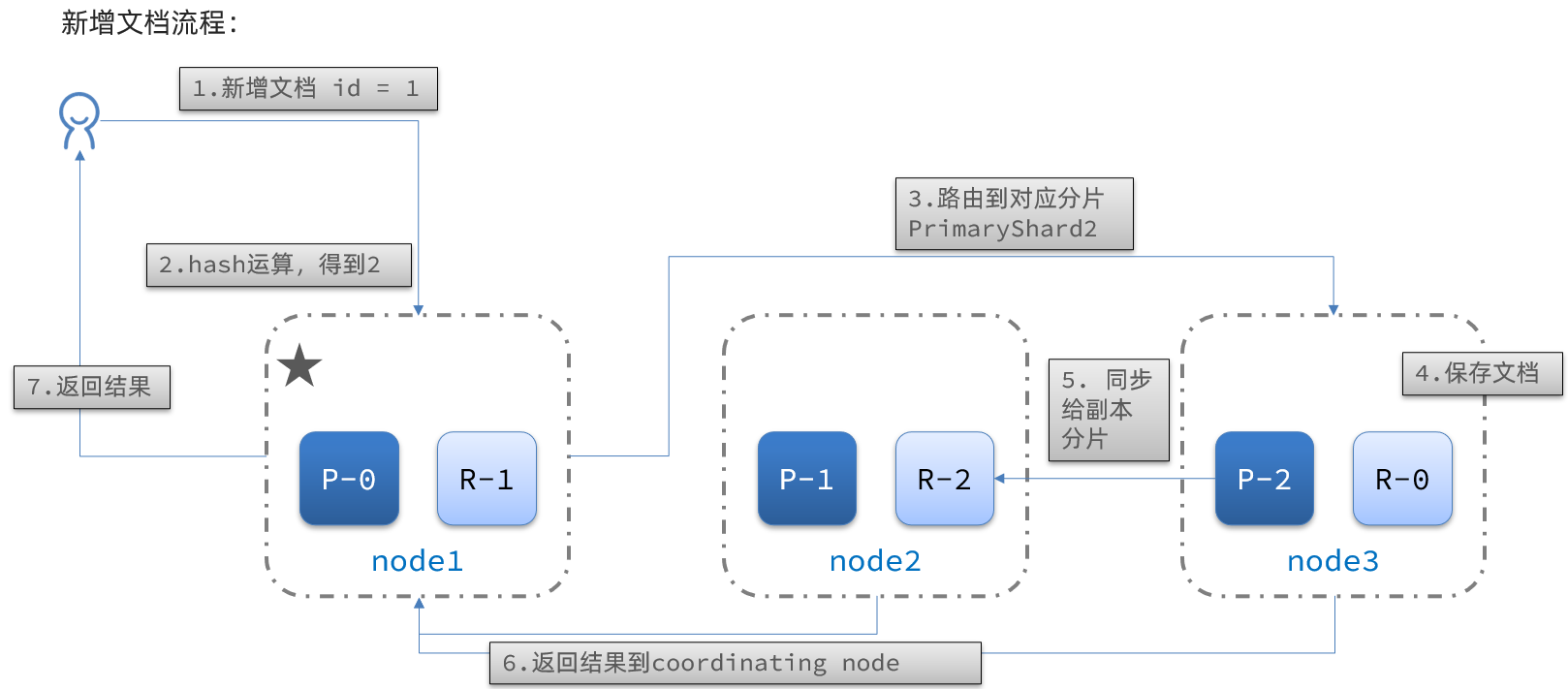
解读:
- 1)新增一个id=1的文档
- 2)对id做hash运算,假如得到的是2,则应该存储到shard-2
- 3)shard-2的主分片在node3节点,将数据路由到node3
- 4)保存文档
- 5)同步给shard-2的副本replica-2,在node2节点
- 6)返回结果给coordinating-node节点
分布式查询
elasticsearch的查询分成两个阶段:
scatter phase:分散阶段,coordinating node会把请求分发到每一个分片
gather phase:聚集阶段,coordinating node汇总data node的搜索结果,并处理为最终结果集返回给用户
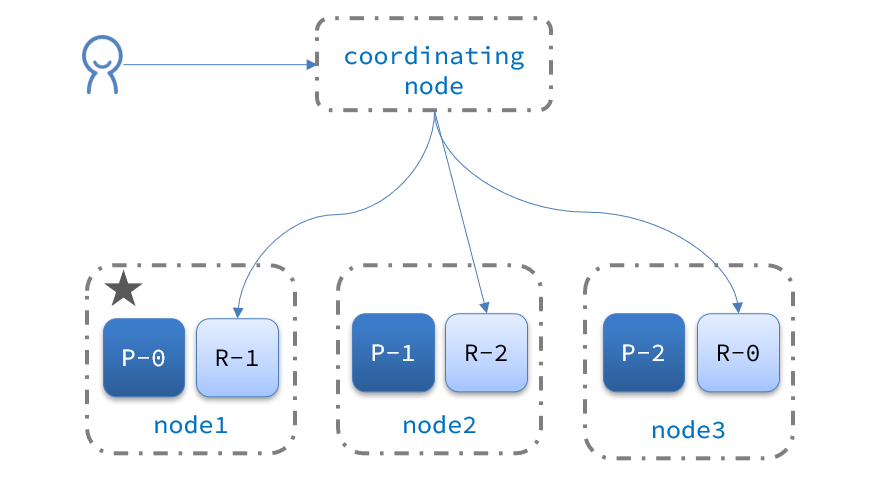
故障转移
集群的master节点会监控集群中的节点状态,如果发现有节点宕机,会立即将宕机节点的分片数据迁移到其它节点,确保数据安全,这个叫做故障转移。
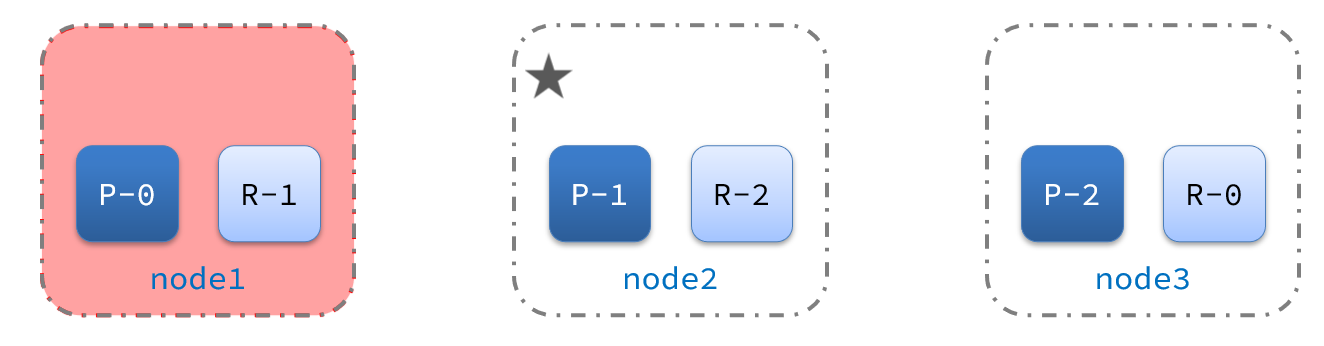
1)例如一个集群结构如图:
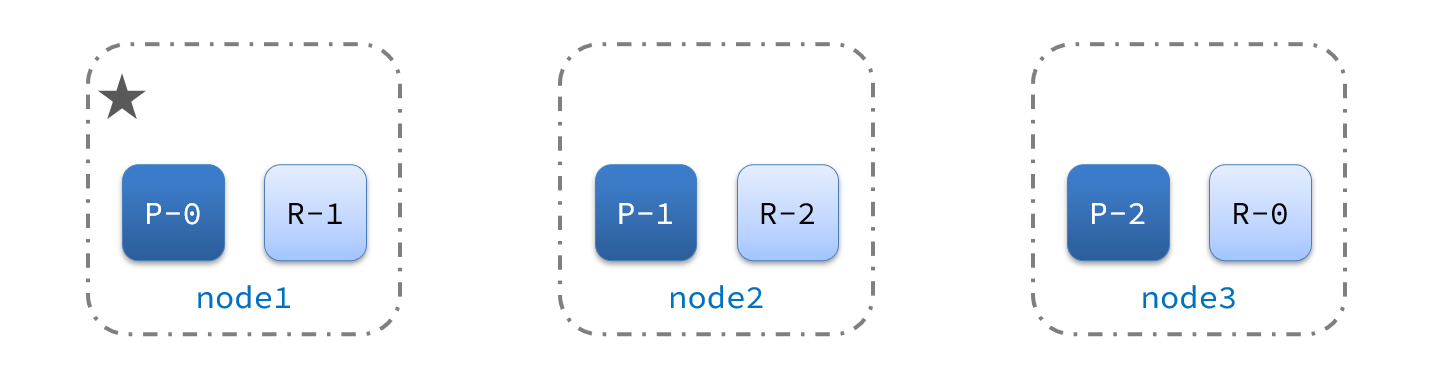
现在,node1是主节点,其它两个节点是从节点。
2)突然,node1发生了故障:
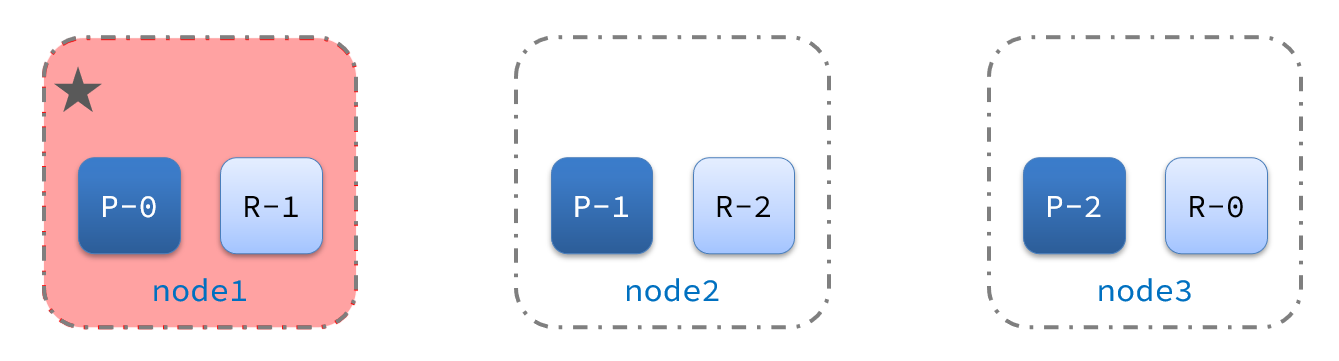
宕机后的第一件事,需要重新选主,例如选中了node2:
node2成为主节点后,会检测集群监控状态,发现:shard-1、shard-0没有副本节点。因此需要将node1上的数据迁移到node2、node3: